Do Far-Right Mayors Promote Informal Healthcare Chauvinism?
Ethnic Discrimination in Access to Basic Healthcare in Italy
Krzysztof Krakowski, Dina Rosenberg, Alessio Romarri, and Merlin Schaeffer
2022-10-24
The far-right and welfare chauvinism
A system of social protection for those who belong to the ethnically defined community
Kitschelt and McGann (1997)
The far-right and welfare chauvinism
A system of social protection for those who belong to the ethnically defined community
Kitschelt and McGann (1997)
Two examples of welfare chauvinistic policy in Denmark:
(Jørgensen and Thomsen, 2016)
Direct: "Start Aid": Ca. 50% lower benefits to refugees & recent immigrants.
Indirect: "225 hour rule": Both partners in a union need to have worked 225+ hours in the past 12 months to qualify for benefits.

The far-right and welfare chauvinism
A system of social protection for those who belong to the ethnically defined community
Kitschelt and McGann (1997)
Danes' public opinion on who should to get vaccinated first
Source: Schaeffer and Haderup Larsen (2022)
The far-right and welfare chauvinism
A system of social protection for those who belong to the ethnically defined community
Kitschelt and McGann (1997)
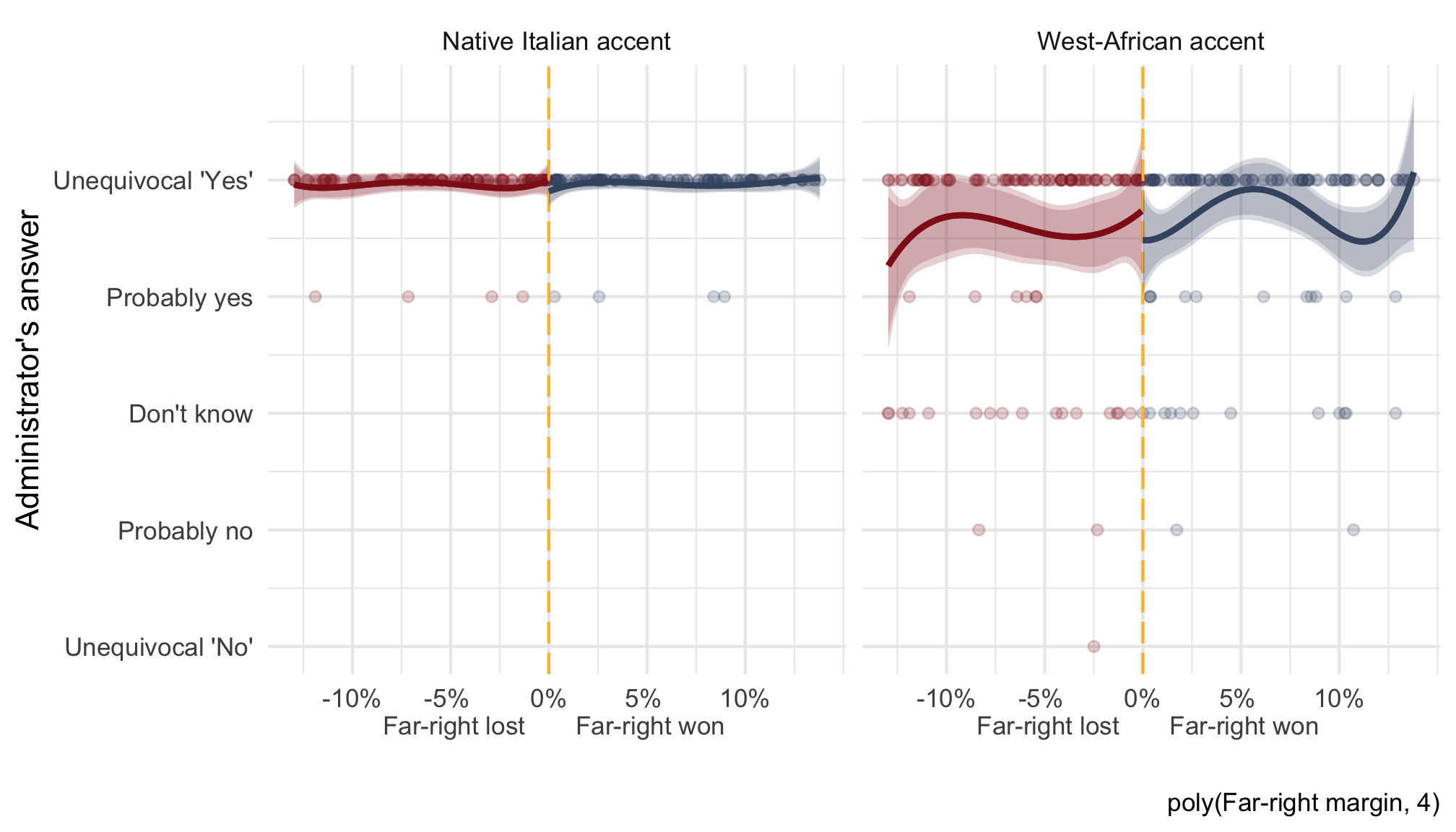
Quality of written answers
from German welfare office administrators
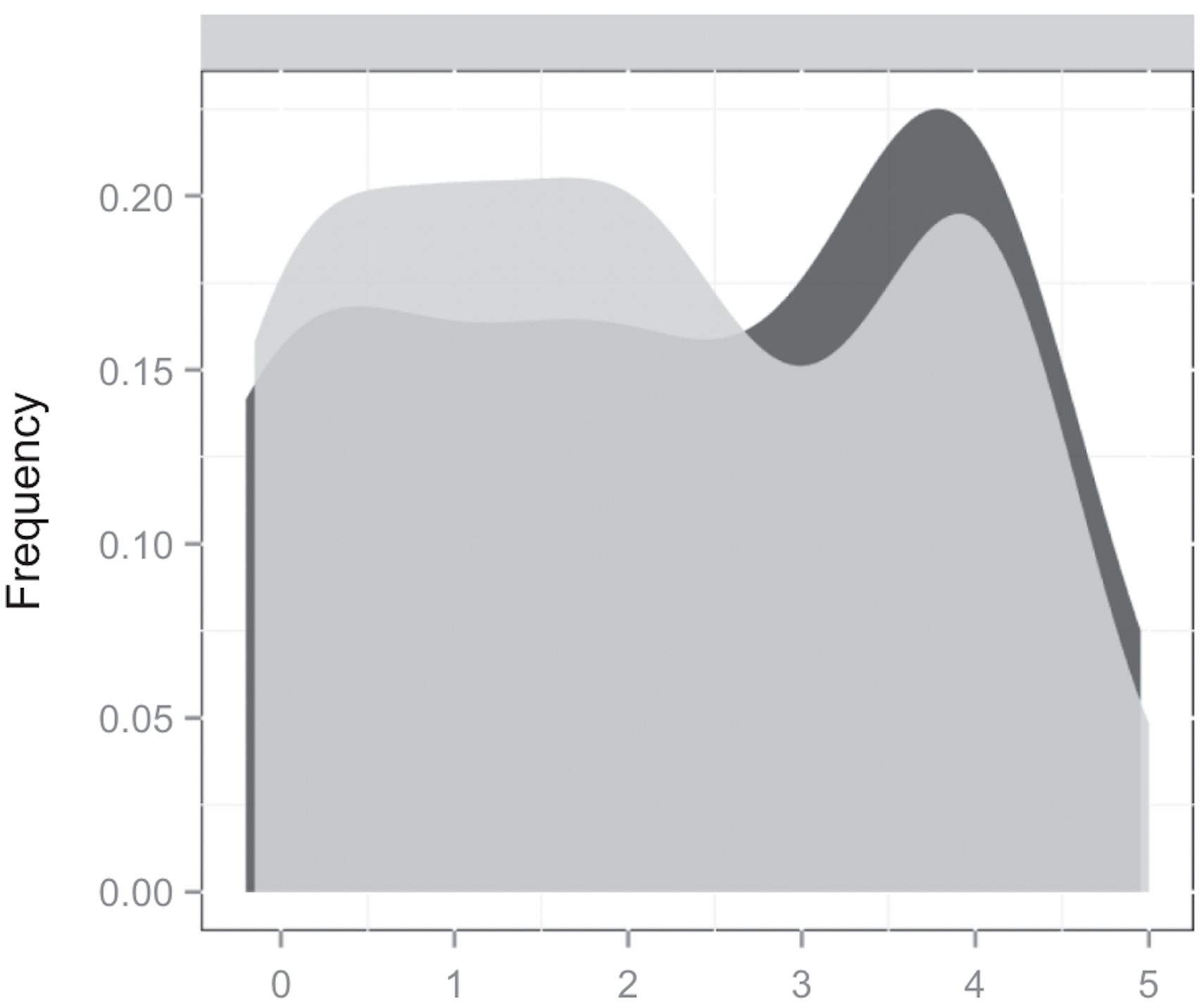 Source: Hemker and Rink (2017)
Source: Hemker and Rink (2017)
Do far-right mayors
promote informal healthcare chauvinism?
Do far-right mayors
promote informal healthcare chauvinism?

Potential mechanisms
- Informal policy.
- Hiring.
- Erosion of social norms.
A field experiment


A field experiment


Research assistants call 200
Italian "Azienda Sanitaria Locale"
to ask for a general practitioner
 Two students with
Two students with
West-African accent
 Two students with
Two students with
native Italian accent
Interview guideline
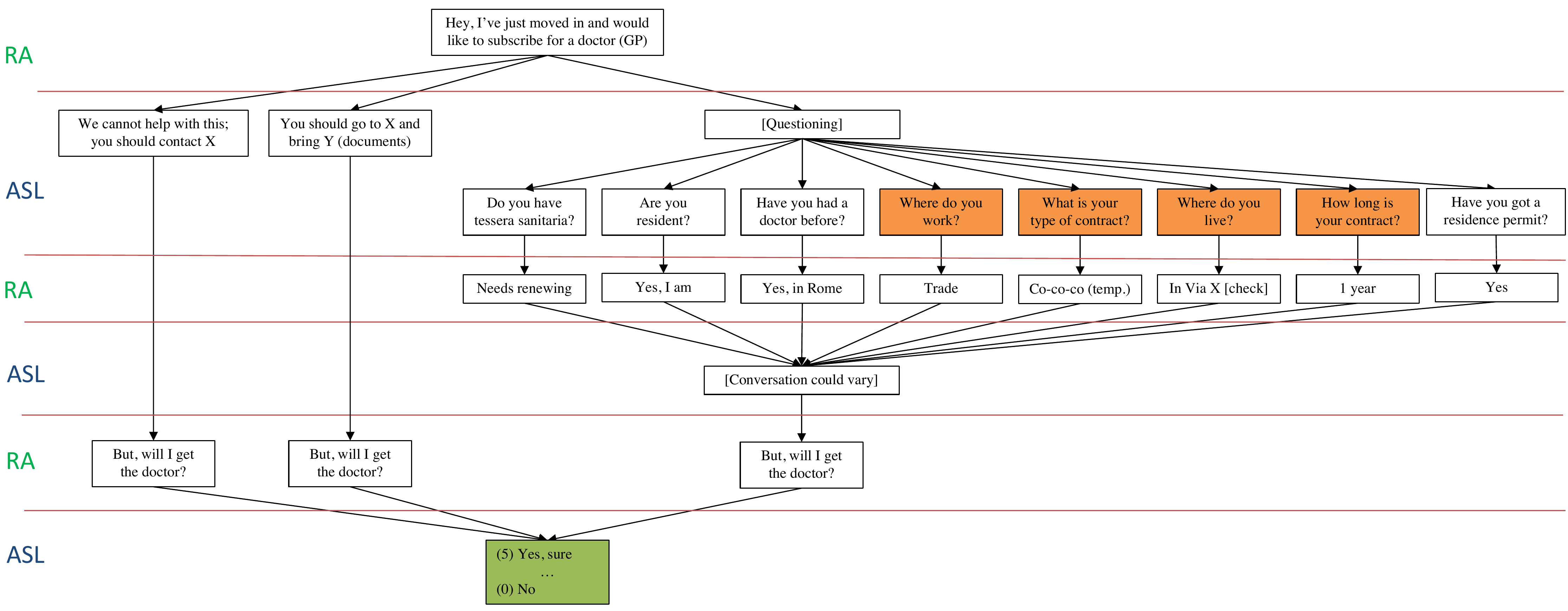
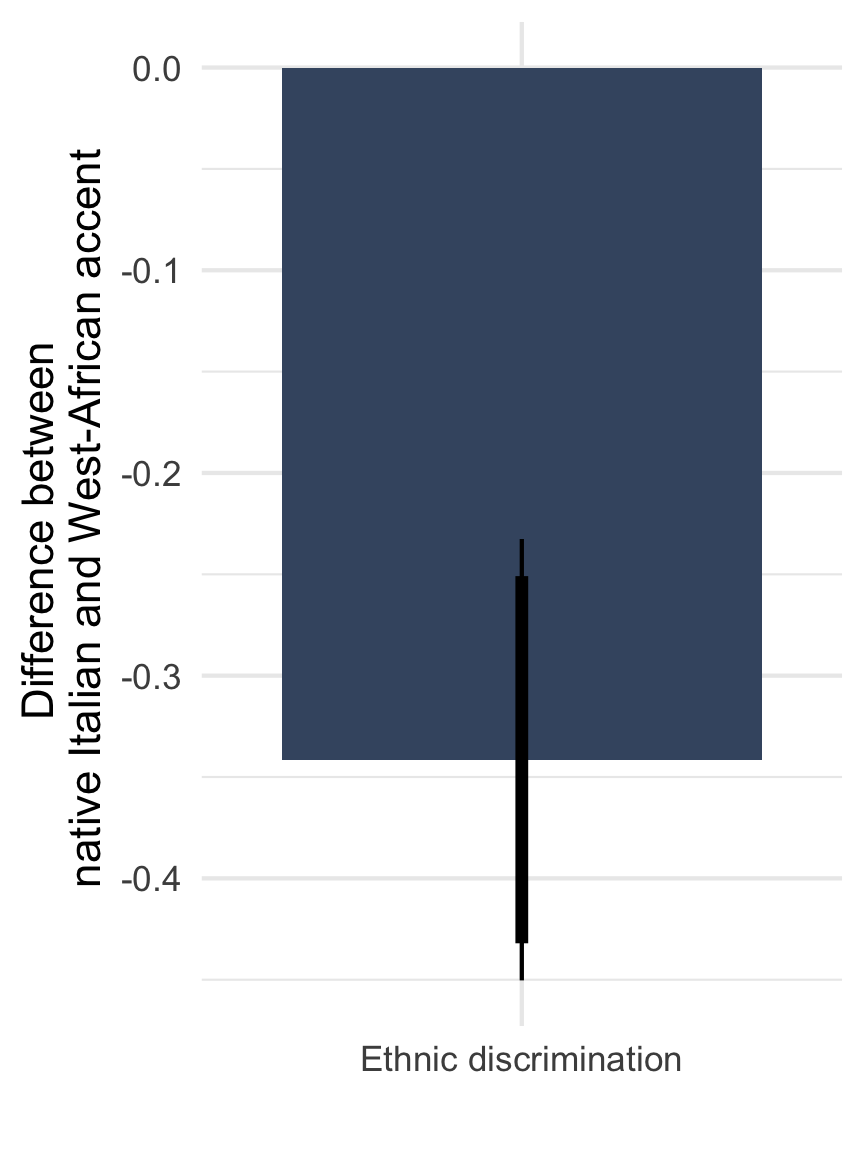
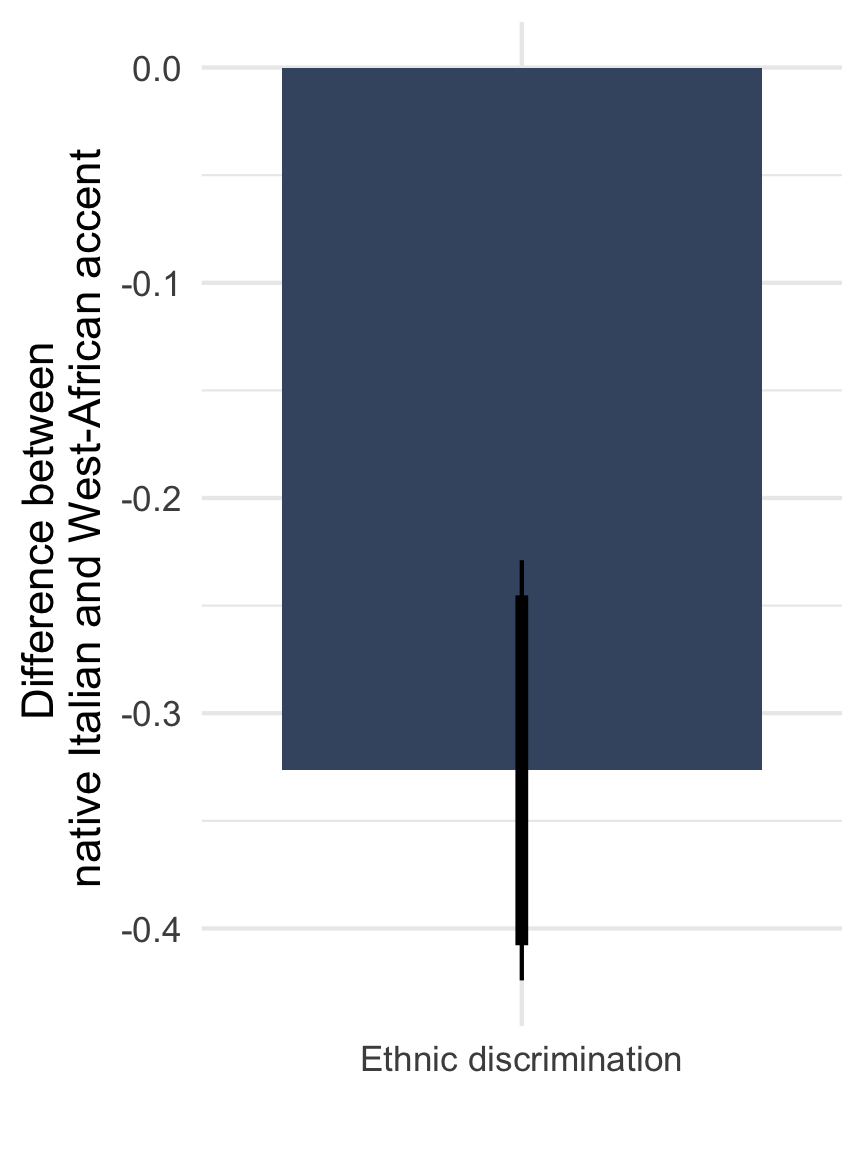
Ethnic discrimination in access to basic healthcare
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Ethnic discrimination in access to basic healthcare
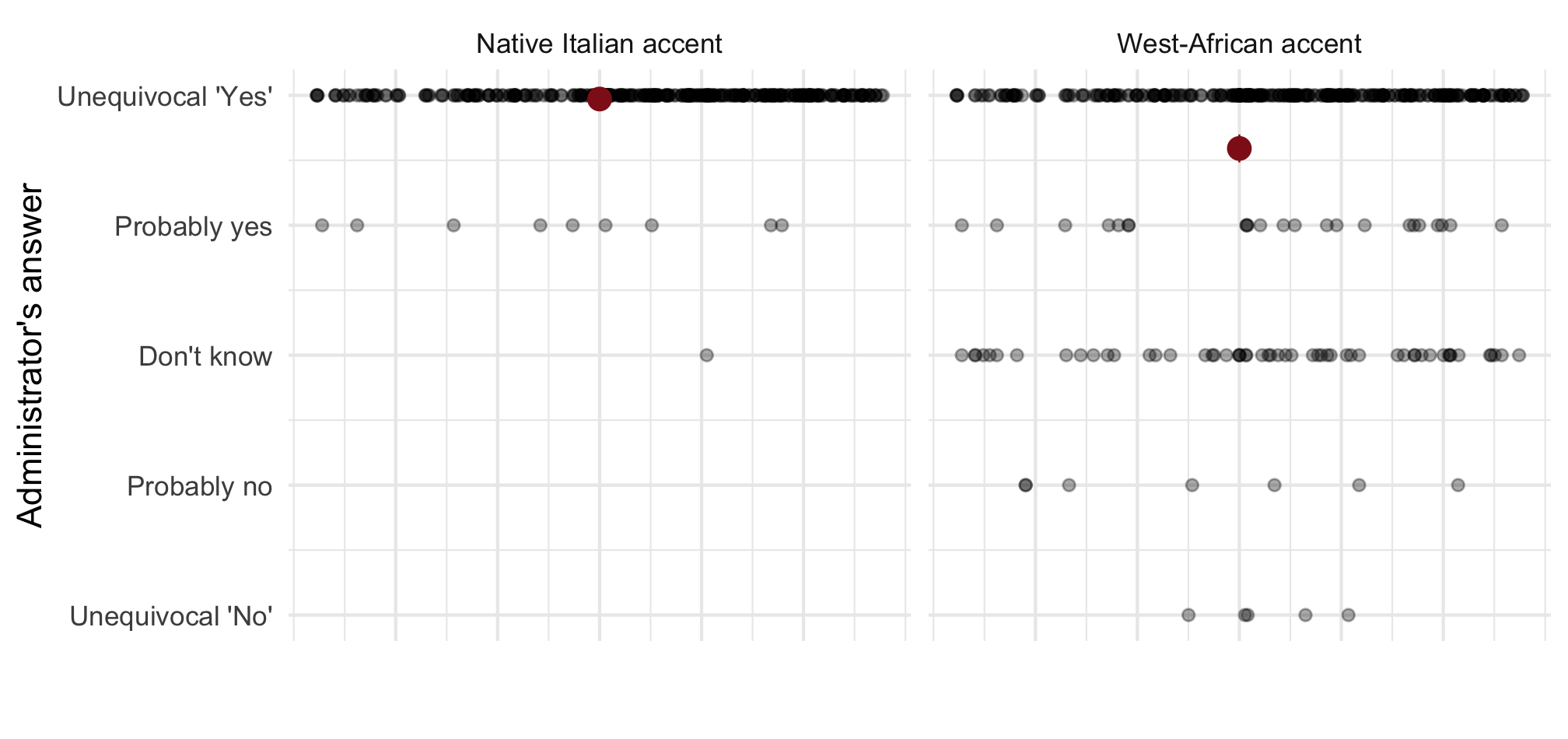
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Ethnic discrimination in access to basic healthcare
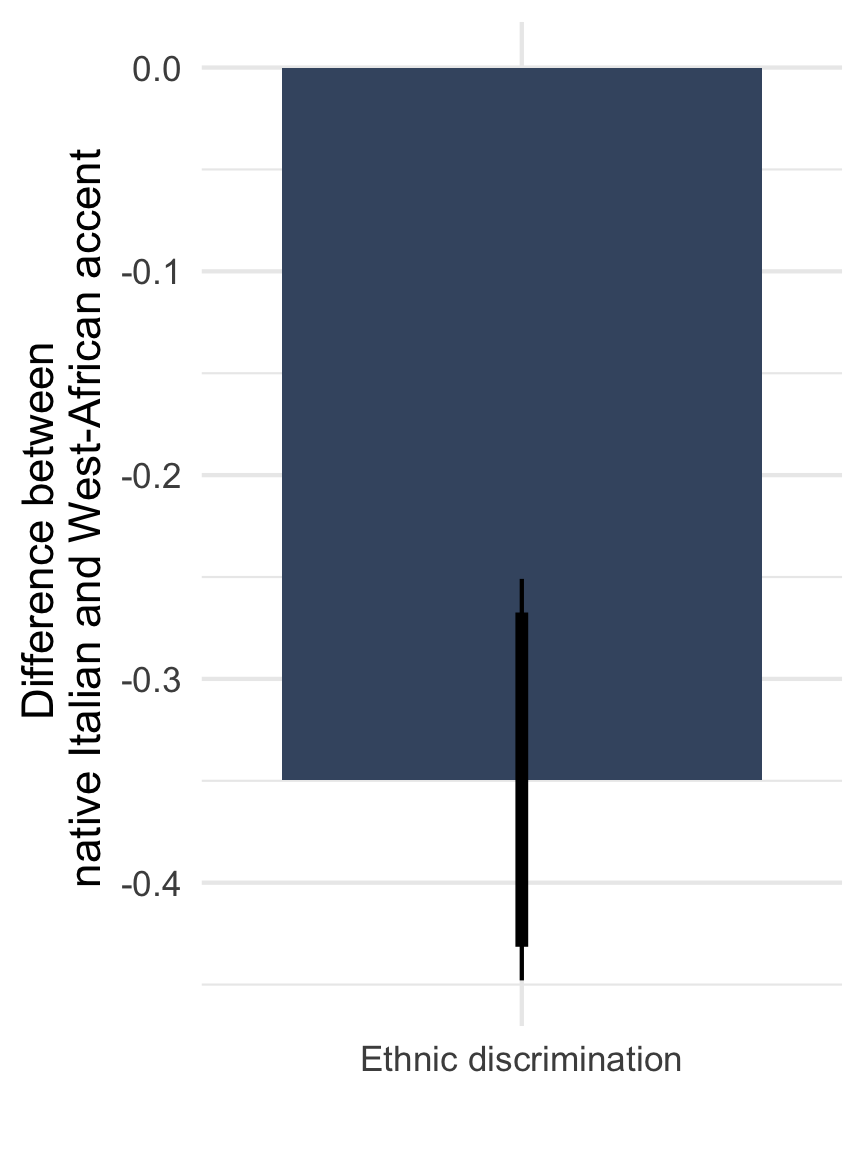
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects.
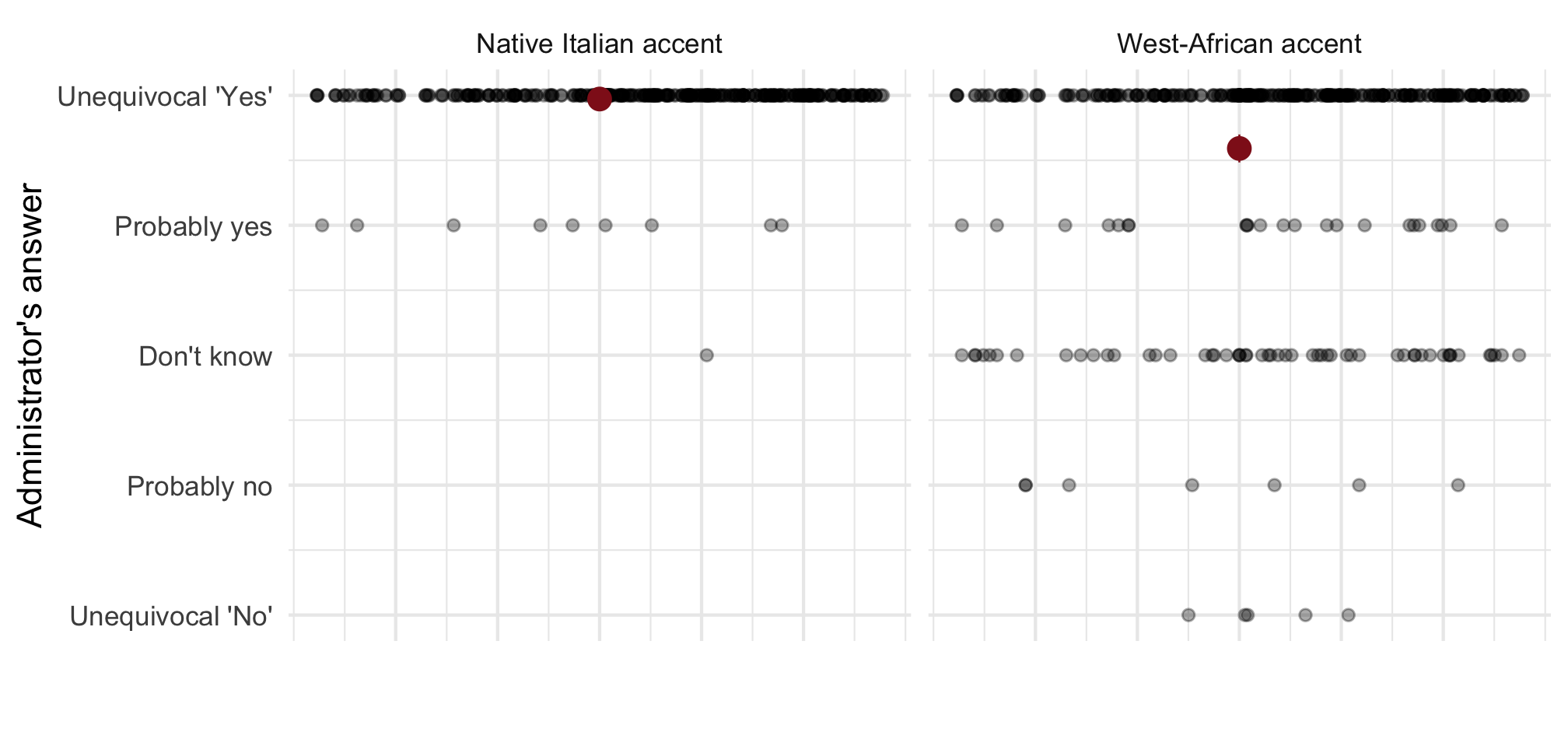
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
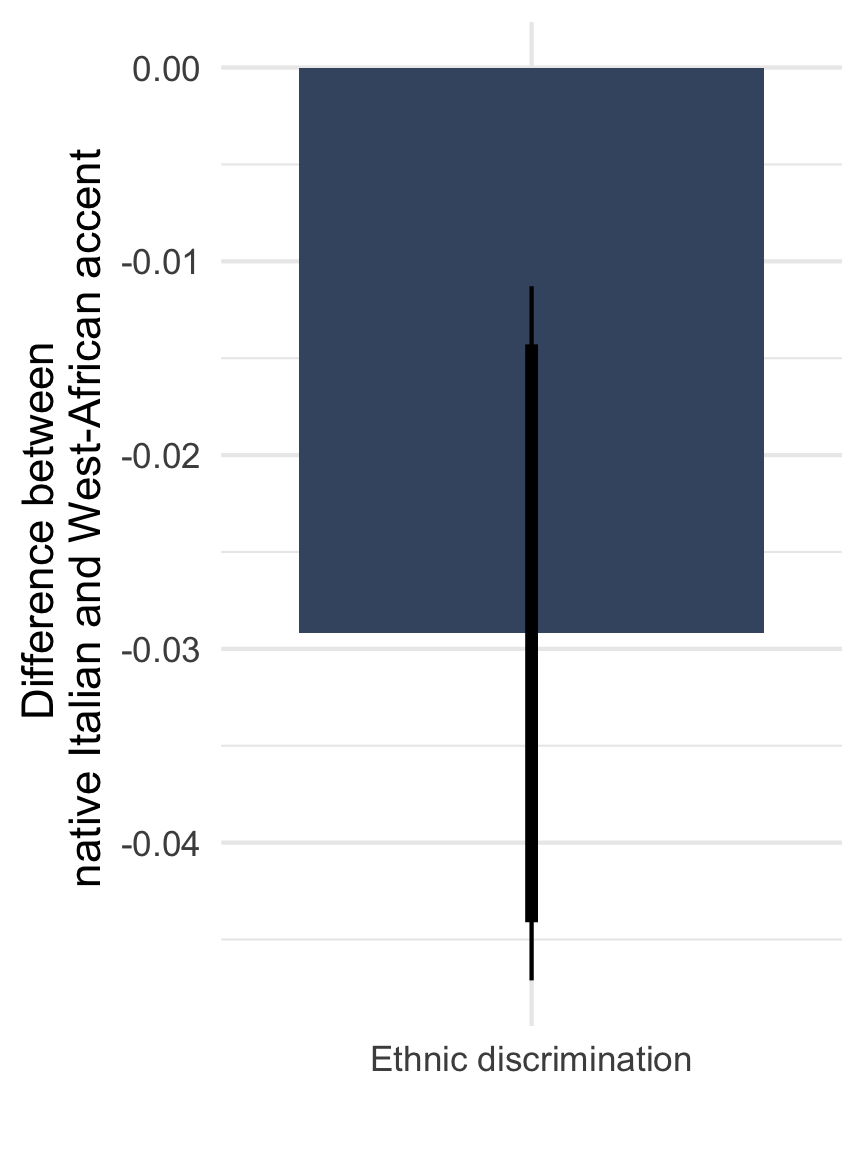
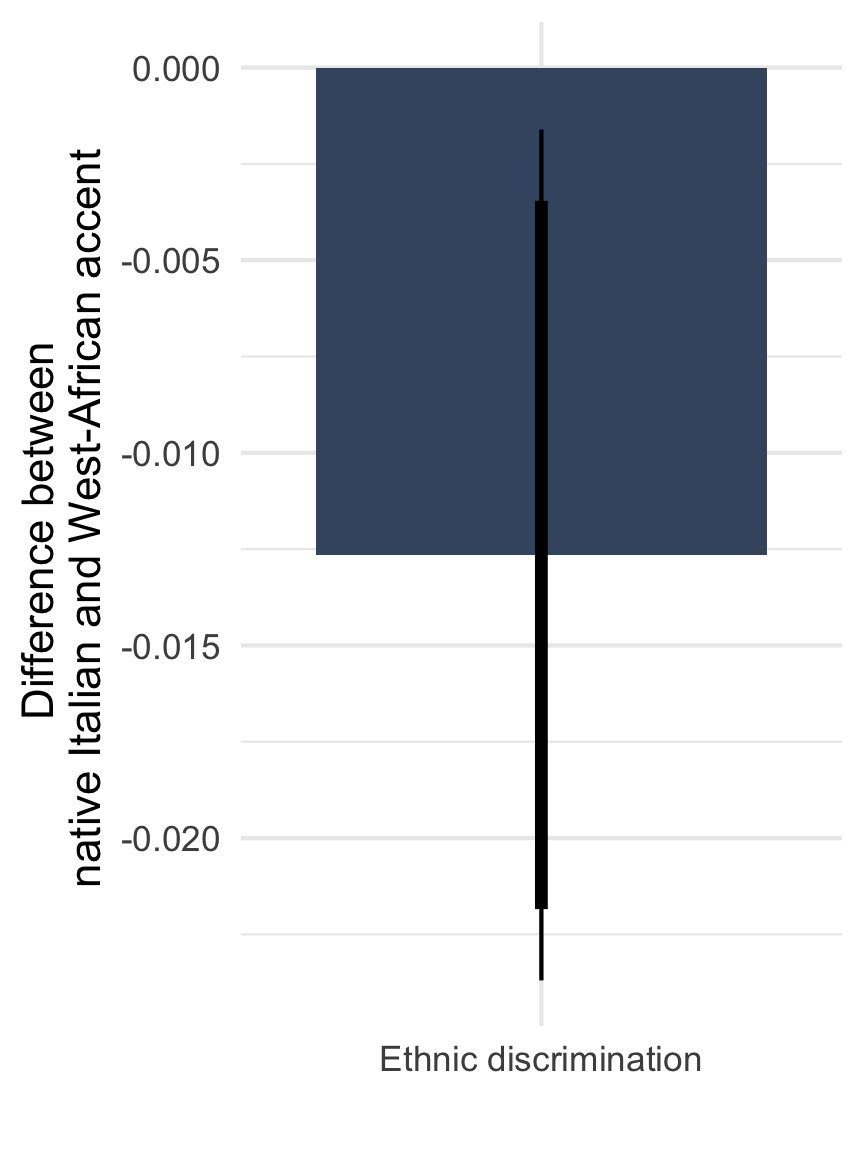
Ethnic discrimination by far-right mayors
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Ethnic discrimination by far-right mayors
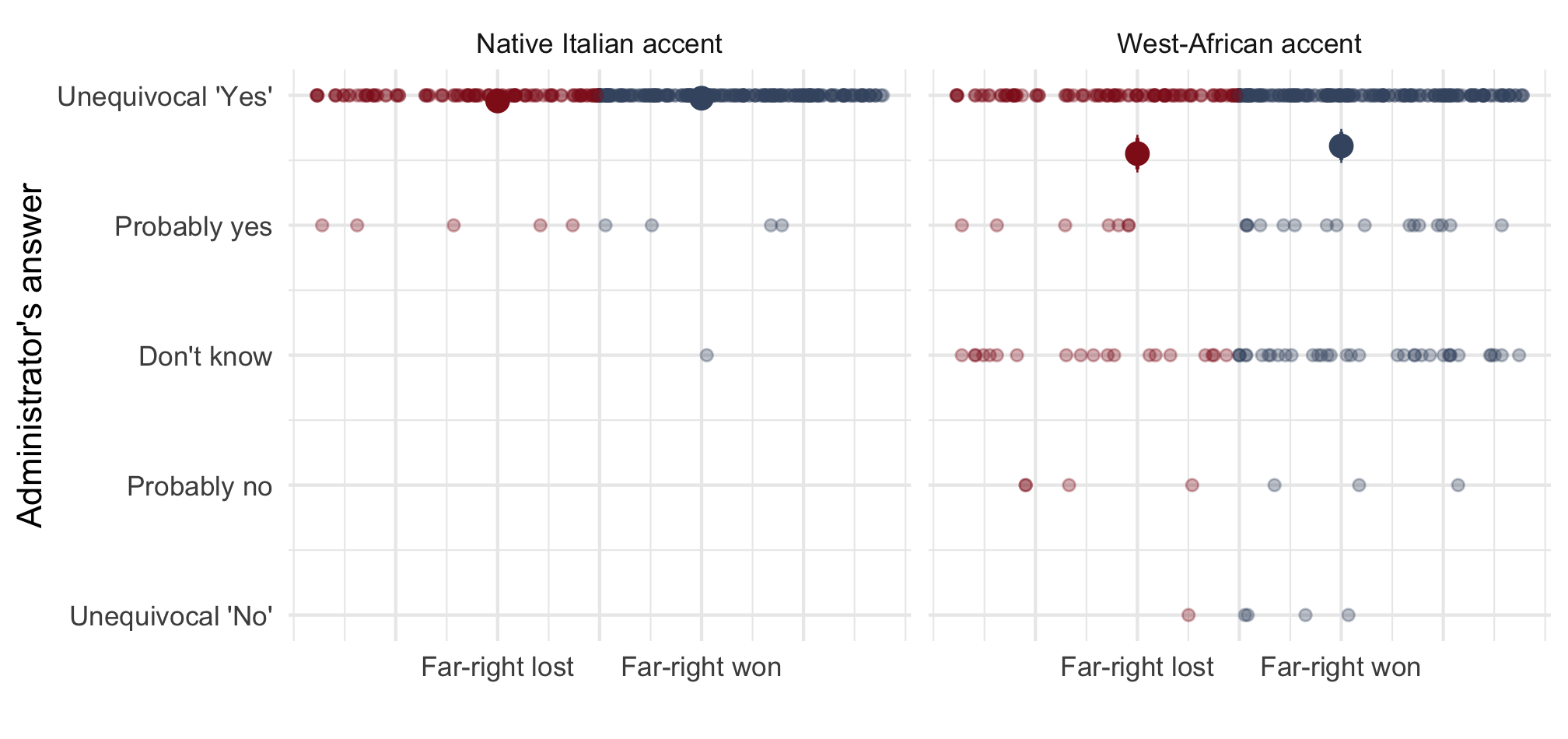
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
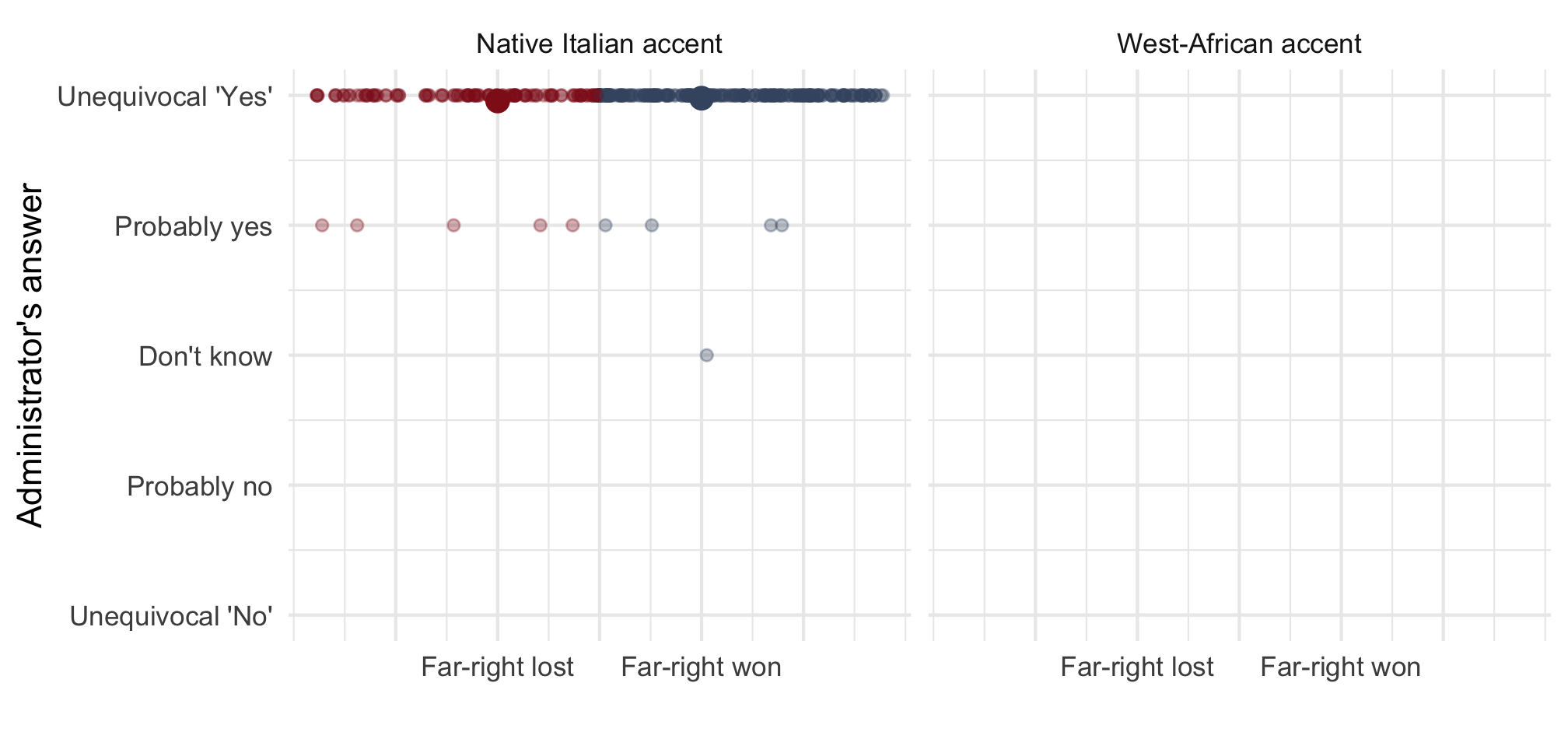
Ethnic discrimination by far-right mayors
Municipalities where far-right candidates ran
versus where they won
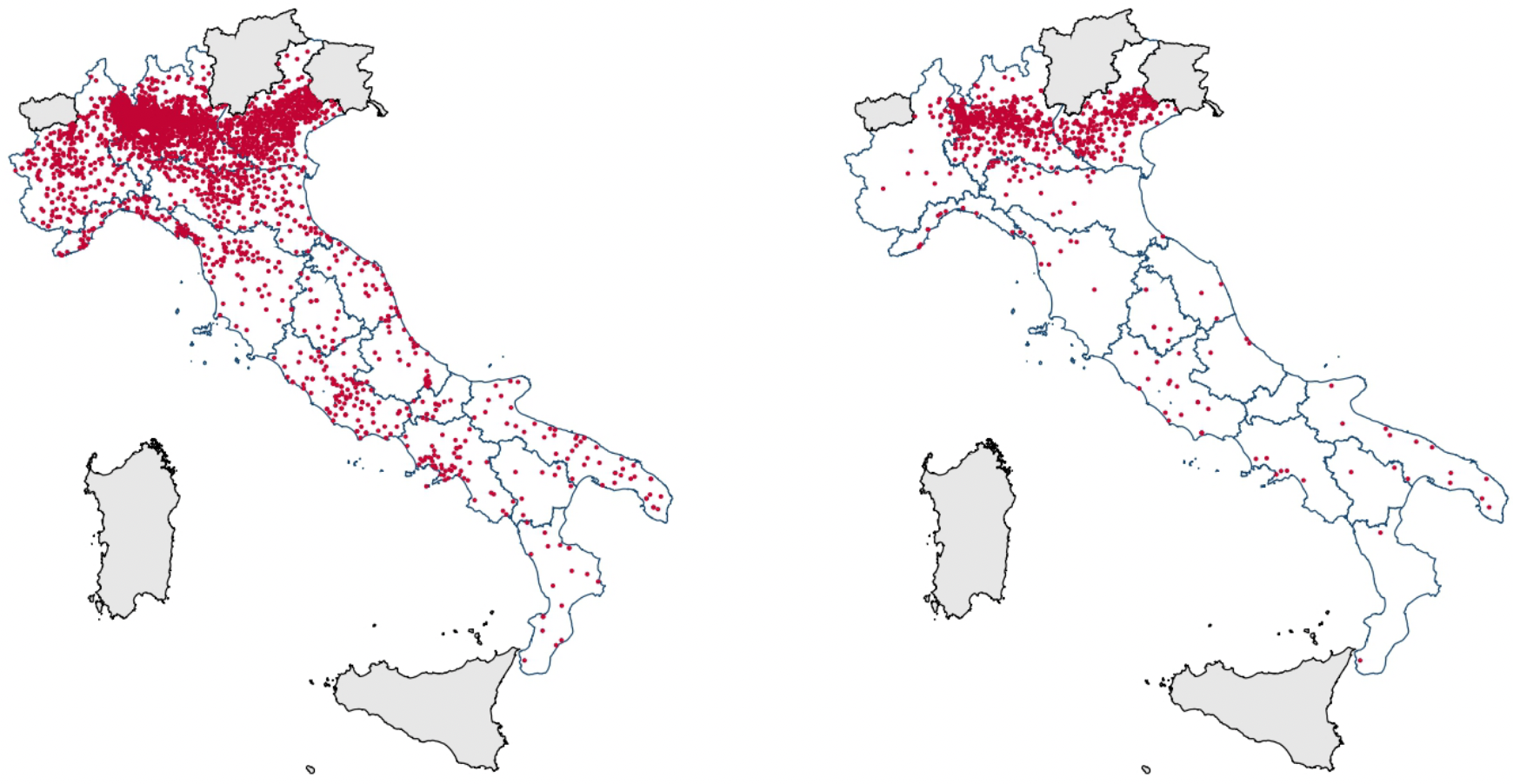 Source: Romarri (2020)
Source: Romarri (2020)
Note: Means with 90 and 95% CI.
n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
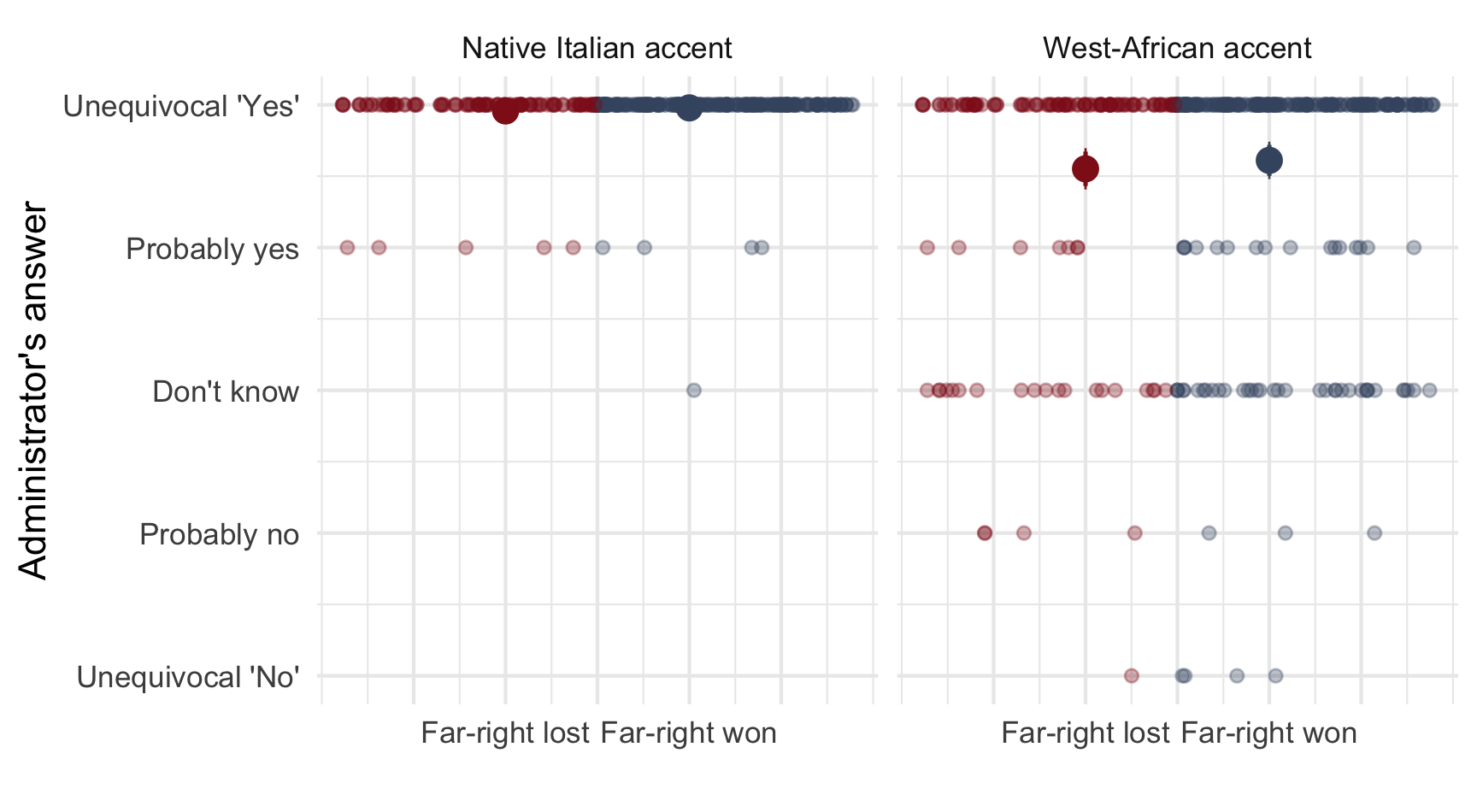
Far-right mayors A regression discontinuity design
Note: n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Balanced confounders around the margin of victory
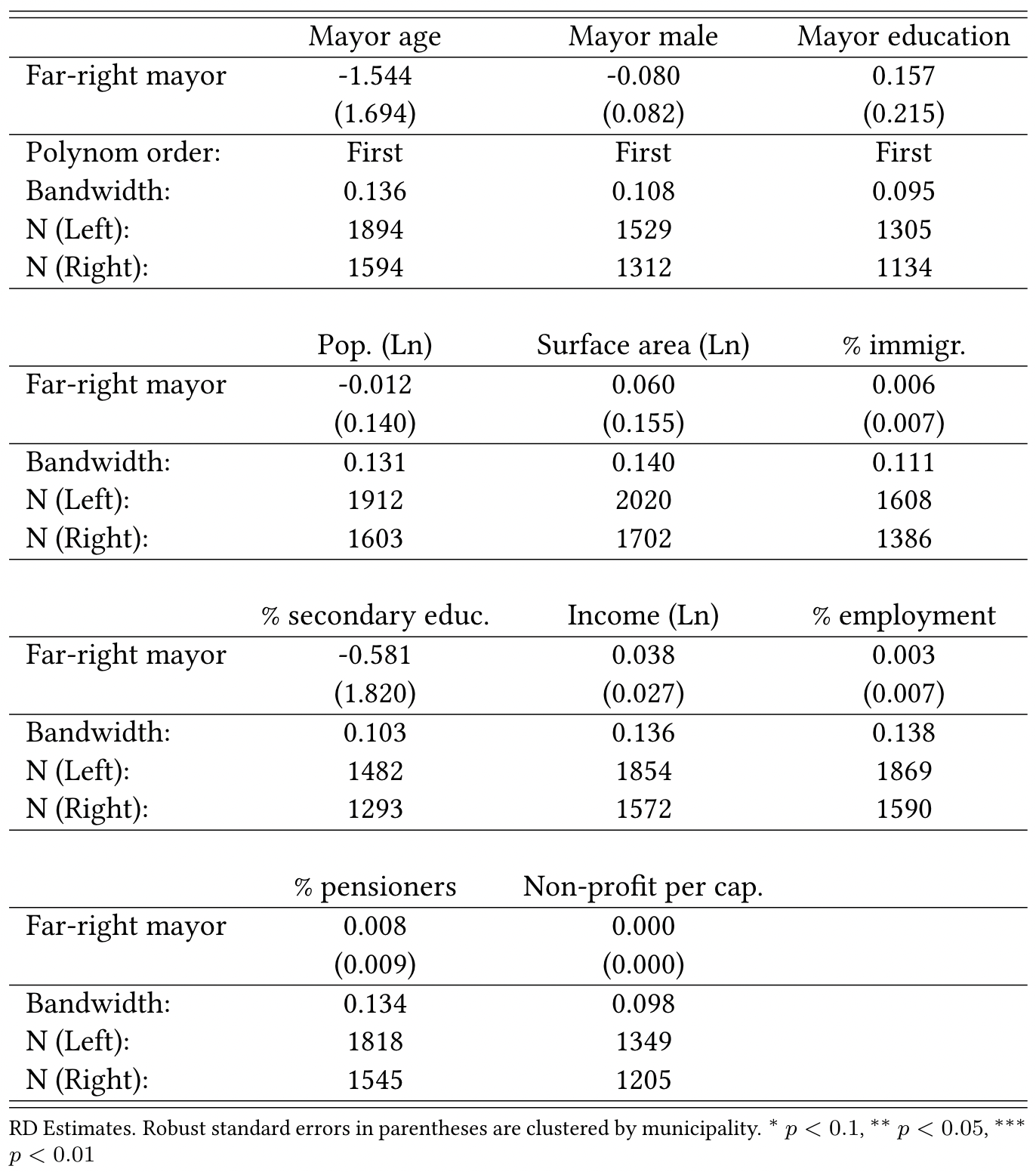 Source: Romarri (2020)
Source: Romarri (2020)
Far-right mayors A regression discontinuity design
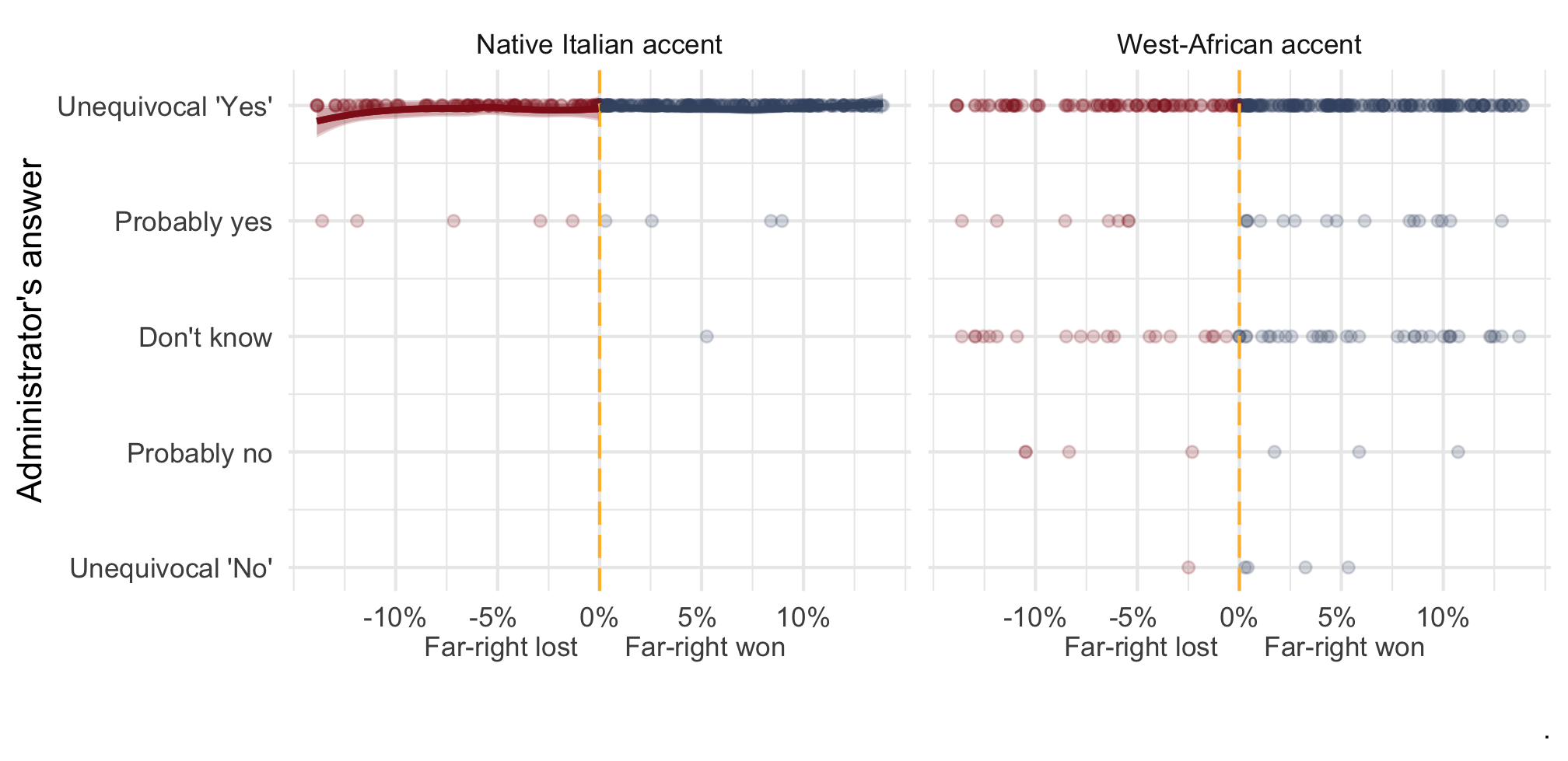
Note: OLS with 90 and 95% CI fitted separately on each side of the margin of victory. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Far-right mayors A regression discontinuity design
Note: OLS with 90 and 95% CI fitted separately on each side of the margin of victory. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
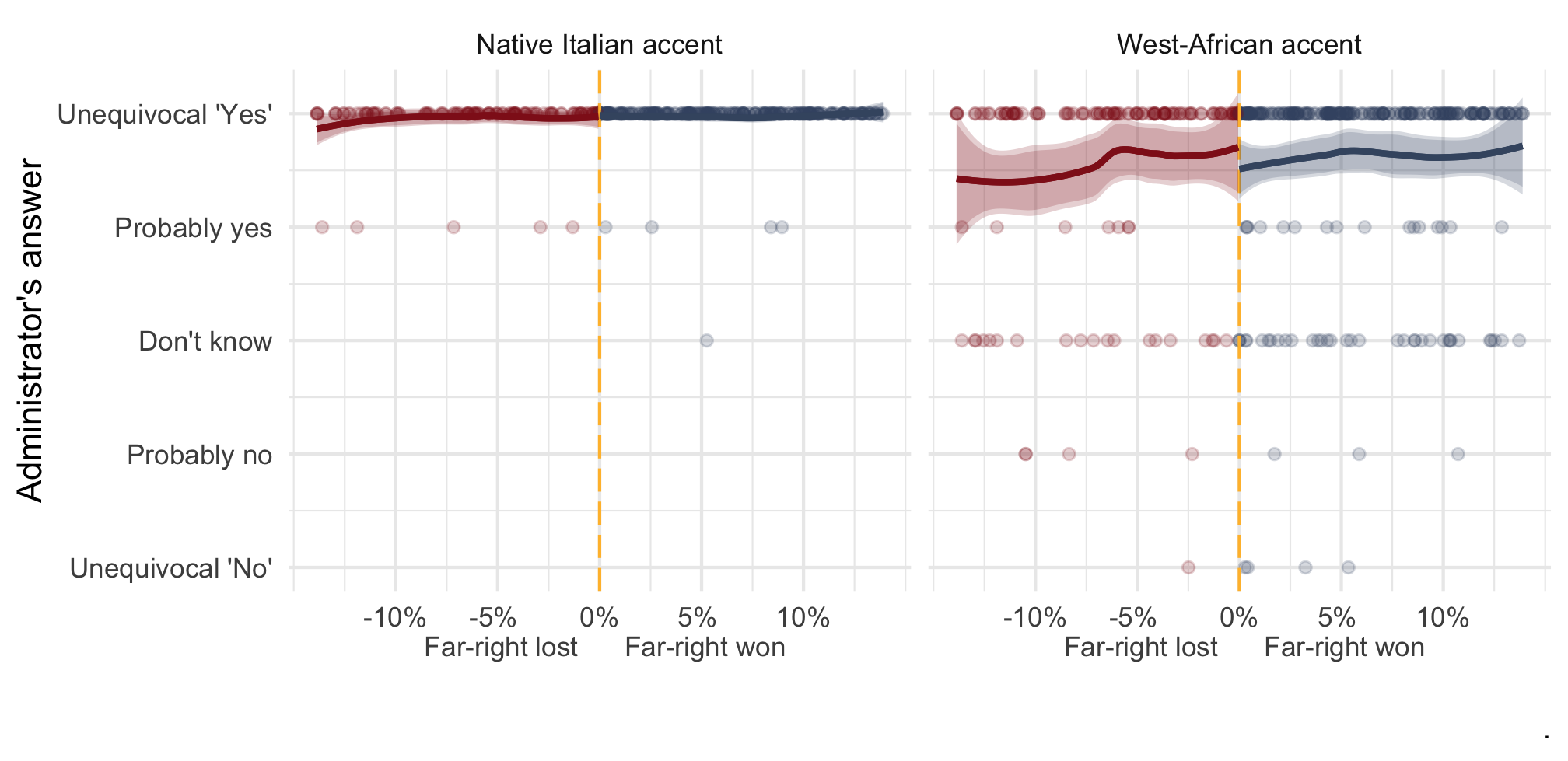
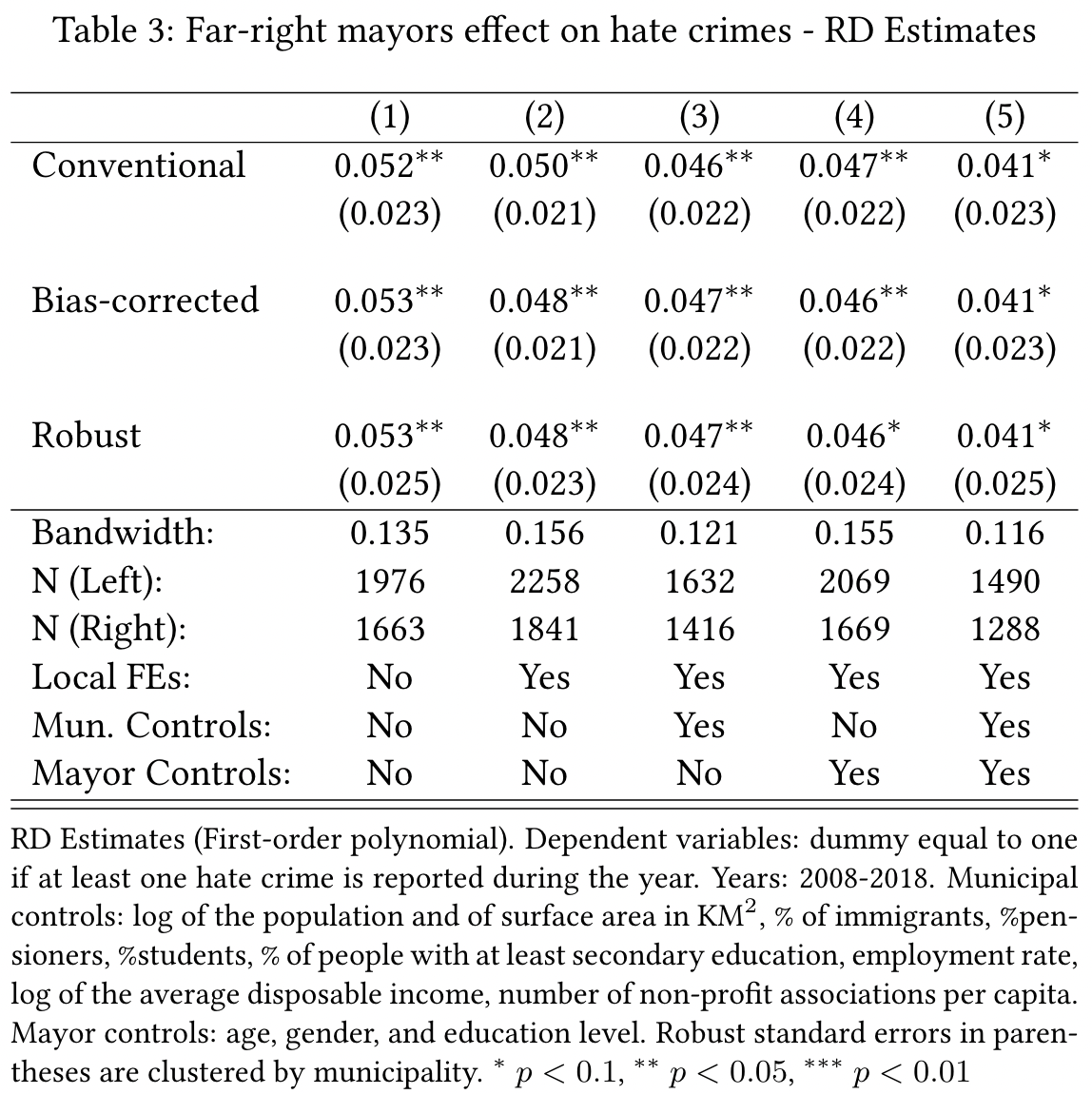
Far-right mayors a Diff-in-RD design
Bias-corrected non-parametric RD with optimized bandwidth (Calonico, Cattaneo, and Titiunik, 2014)
RD among callers with native Italian accent
# Sharp RD estimates using local polynomial regression.# # Number of Obs. 391# BW type mserd# Kernel Triangular# VCE method NN# # Number of Obs. 116 275# Eff. Number of Obs. 32 88# Order est. (p) 1 1# Order bias (q) 2 2# BW est. (h) 3.035 3.035# BW bias (b) 6.032 6.032# rho (h/b) 0.503 0.503# # =============================================================================# Method Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [ 95% C.I. ] # =============================================================================# Conventional -0.026 0.021 -1.257 0.209 [-0.066 , 0.014] # Bias-Corrected -0.039 0.021 -1.892 0.058 [-0.079 , 0.001] # Robust -0.039 0.023 -1.669 0.095 [-0.085 , 0.007] # =============================================================================Far-right mayors a Diff-in-RD design
Bias-corrected non-parametric RD with optimized bandwidth (Calonico, Cattaneo, and Titiunik, 2014)
RD among callers with native Italian accent
# Sharp RD estimates using local polynomial regression.# # Number of Obs. 391# BW type mserd# Kernel Triangular# VCE method NN# # Number of Obs. 116 275# Eff. Number of Obs. 32 88# Order est. (p) 1 1# Order bias (q) 2 2# BW est. (h) 3.035 3.035# BW bias (b) 6.032 6.032# rho (h/b) 0.503 0.503# # =============================================================================# Method Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [ 95% C.I. ] # =============================================================================# Conventional -0.026 0.021 -1.257 0.209 [-0.066 , 0.014] # Bias-Corrected -0.039 0.021 -1.892 0.058 [-0.079 , 0.001] # Robust -0.039 0.023 -1.669 0.095 [-0.085 , 0.007] # =============================================================================RD among callers with West-African accent
# Sharp RD estimates using local polynomial regression.# # Number of Obs. 421# BW type mserd# Kernel Triangular# VCE method NN# # Number of Obs. 136 285# Eff. Number of Obs. 26 72# Order est. (p) 1 1# Order bias (q) 2 2# BW est. (h) 2.330 2.330# BW bias (b) 4.301 4.301# rho (h/b) 0.542 0.542# # =============================================================================# Method Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [ 95% C.I. ] # =============================================================================# Conventional -0.536 0.178 -3.012 0.003 [-0.885 , -0.187] # Bias-Corrected -0.616 0.178 -3.457 0.001 [-0.964 , -0.267] # Robust -0.616 0.196 -3.146 0.002 [-0.999 , -0.232] # =============================================================================Far-right mayors a Diff-in-RD design
Bias-corrected non-parametric RD with optimized bandwidth (Calonico, Cattaneo, and Titiunik, 2014)
RD among callers with native Italian accent
# Sharp RD estimates using local polynomial regression.# # Number of Obs. 391# BW type mserd# Kernel Triangular# VCE method NN# # Number of Obs. 116 275# Eff. Number of Obs. 32 88# Order est. (p) 1 1# Order bias (q) 2 2# BW est. (h) 3.035 3.035# BW bias (b) 6.032 6.032# rho (h/b) 0.503 0.503# # =============================================================================# Method Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [ 95% C.I. ] # =============================================================================# Conventional -0.026 0.021 -1.257 0.209 [-0.066 , 0.014] # Bias-Corrected -0.039 0.021 -1.892 0.058 [-0.079 , 0.001] # Robust -0.039 0.023 -1.669 0.095 [-0.085 , 0.007] # =============================================================================RD among callers with West-African accent
# Sharp RD estimates using local polynomial regression.# # Number of Obs. 421# BW type mserd# Kernel Triangular# VCE method NN# # Number of Obs. 136 285# Eff. Number of Obs. 26 72# Order est. (p) 1 1# Order bias (q) 2 2# BW est. (h) 2.330 2.330# BW bias (b) 4.301 4.301# rho (h/b) 0.542 0.542# # =============================================================================# Method Coef. Std. Err. z P>|z| [ 95% C.I. ] # =============================================================================# Conventional -0.536 0.178 -3.012 0.003 [-0.885 , -0.187] # Bias-Corrected -0.616 0.178 -3.457 0.001 [-0.964 , -0.267] # Robust -0.616 0.196 -3.146 0.002 [-0.999 , -0.232] # =============================================================================ΔRDD=−0.616−(−0.039)=−0.577
Far-right mayors a Diff-in-RD design
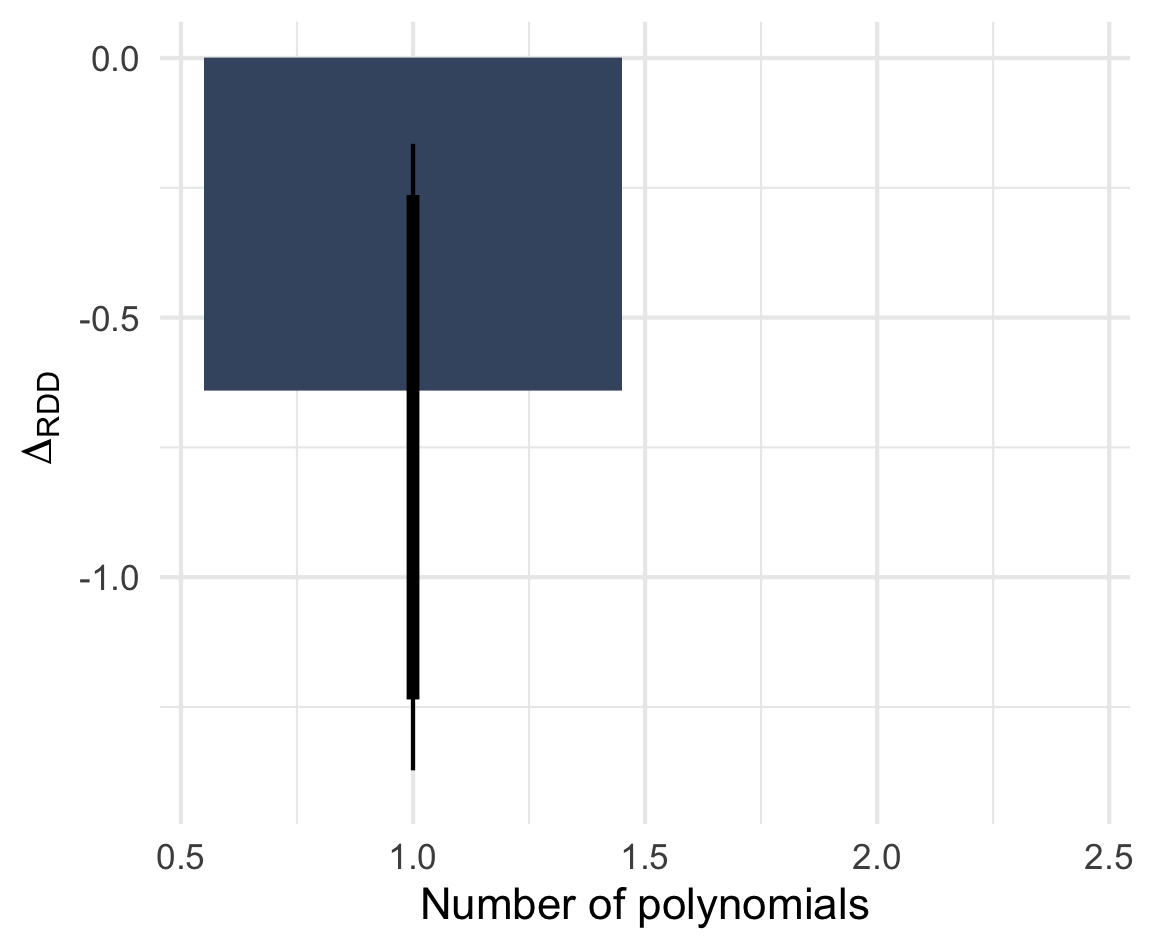
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Far-right mayors a Diff-in-RD design
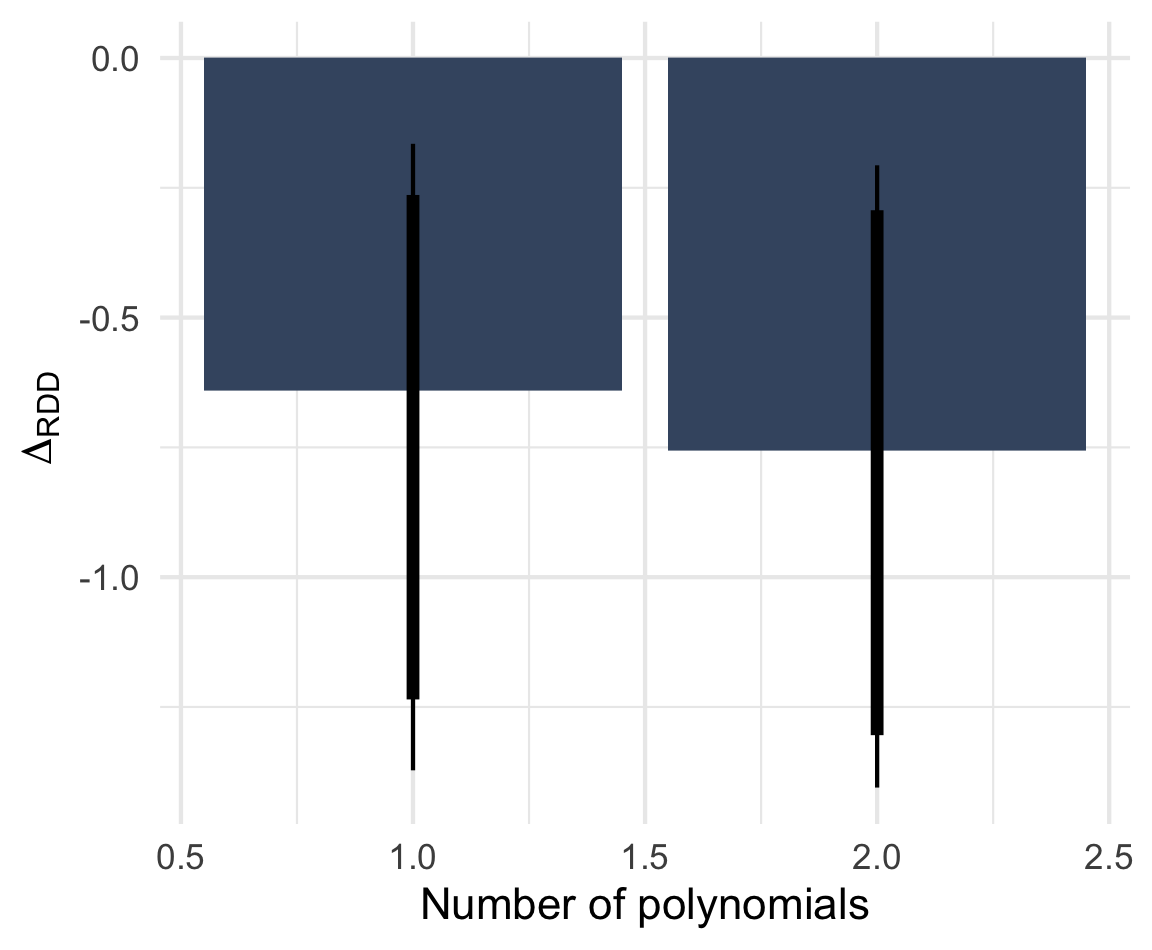
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Nr. of questions asked by administrator (0 - 10)
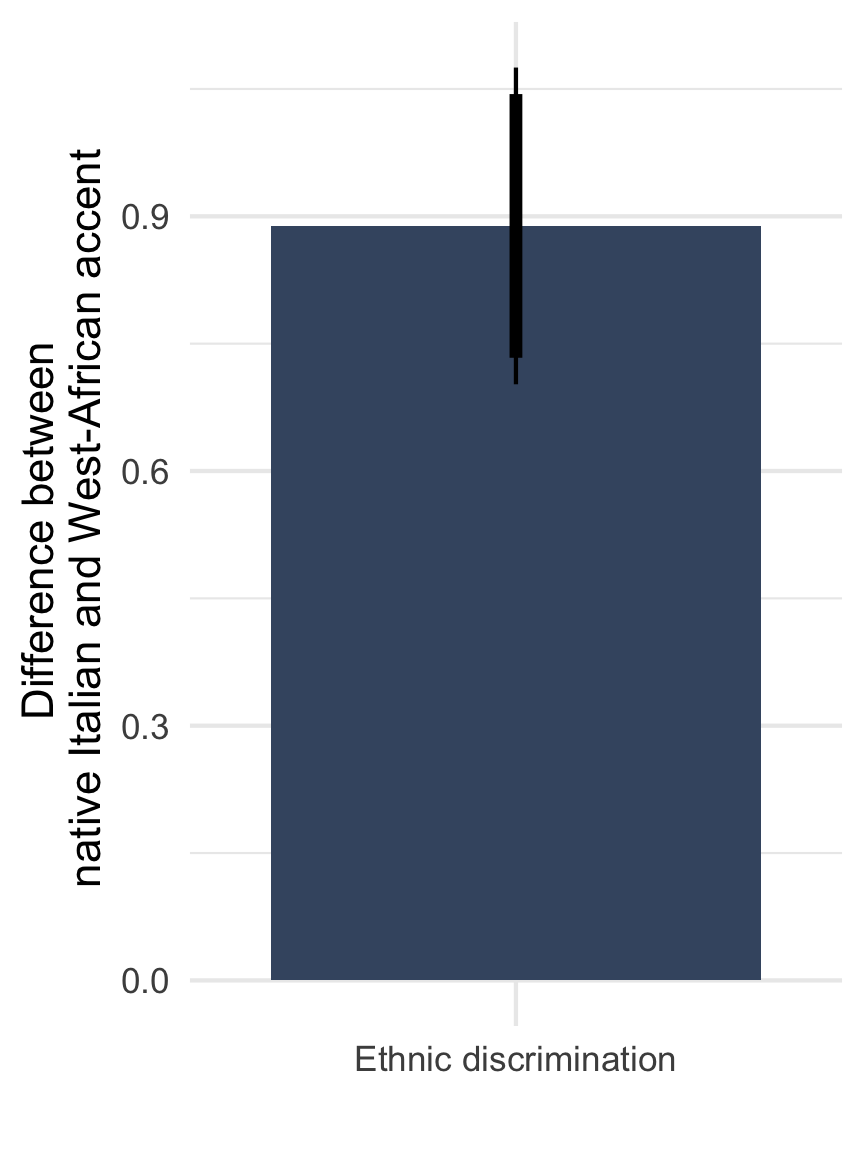
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 806 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 415) to 252 municipalities.
Nr. of questions asked by administrator (0 - 10)

Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 806 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 415) to 252 municipalities.
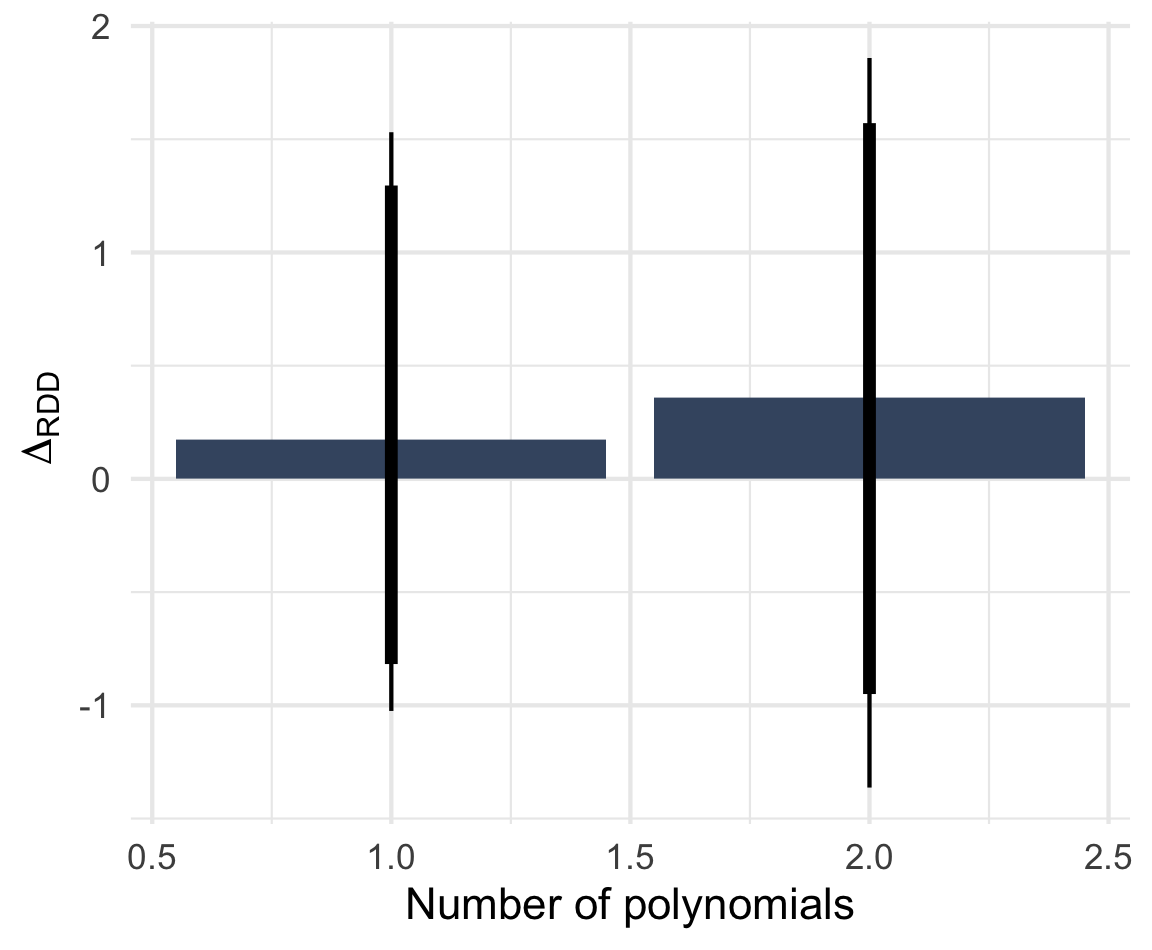
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent. n = 806 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 415) to 252 municipalities.
Nr. of irrelevant questions asked by administrator (0 - 4)
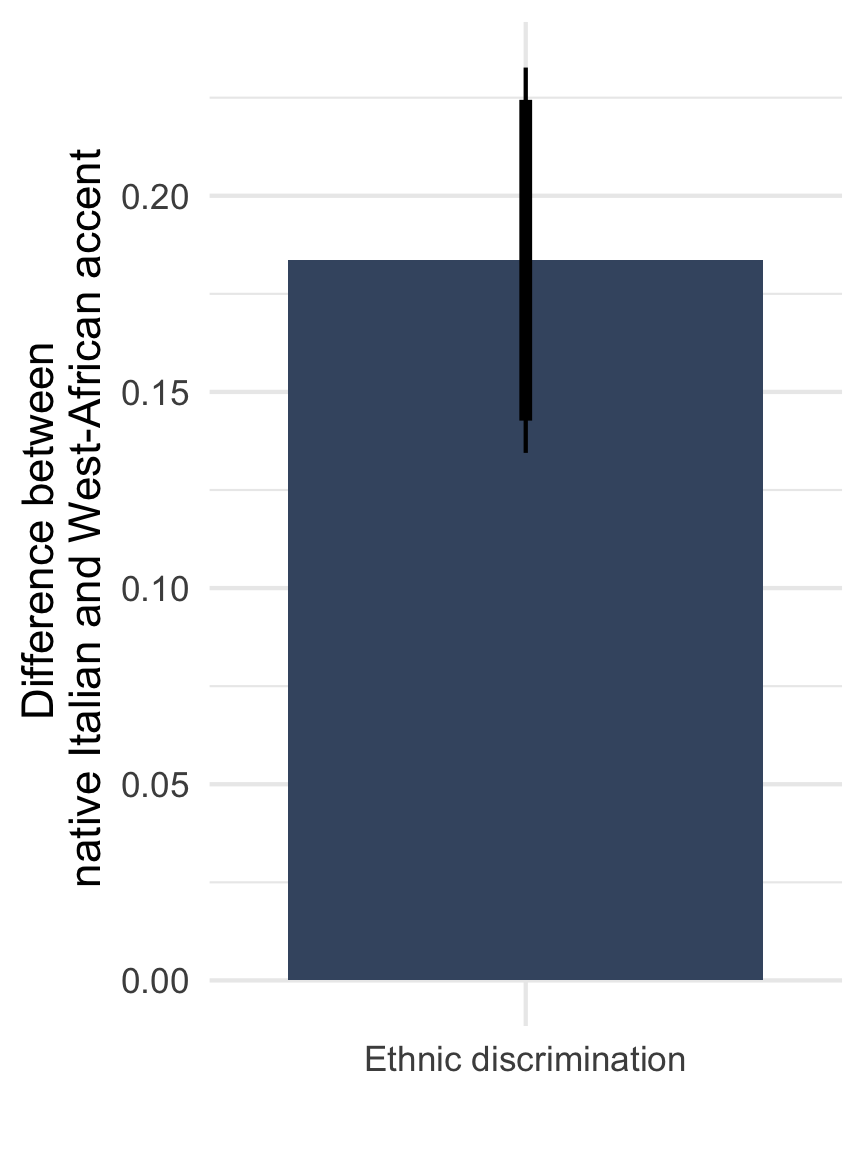
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 805 telephone calls (resp. 392 & 413) to 252 municipalities.
Nr. of irrelevant questions asked by administrator (0 - 4)

Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 805 telephone calls (resp. 392 & 413) to 252 municipalities.
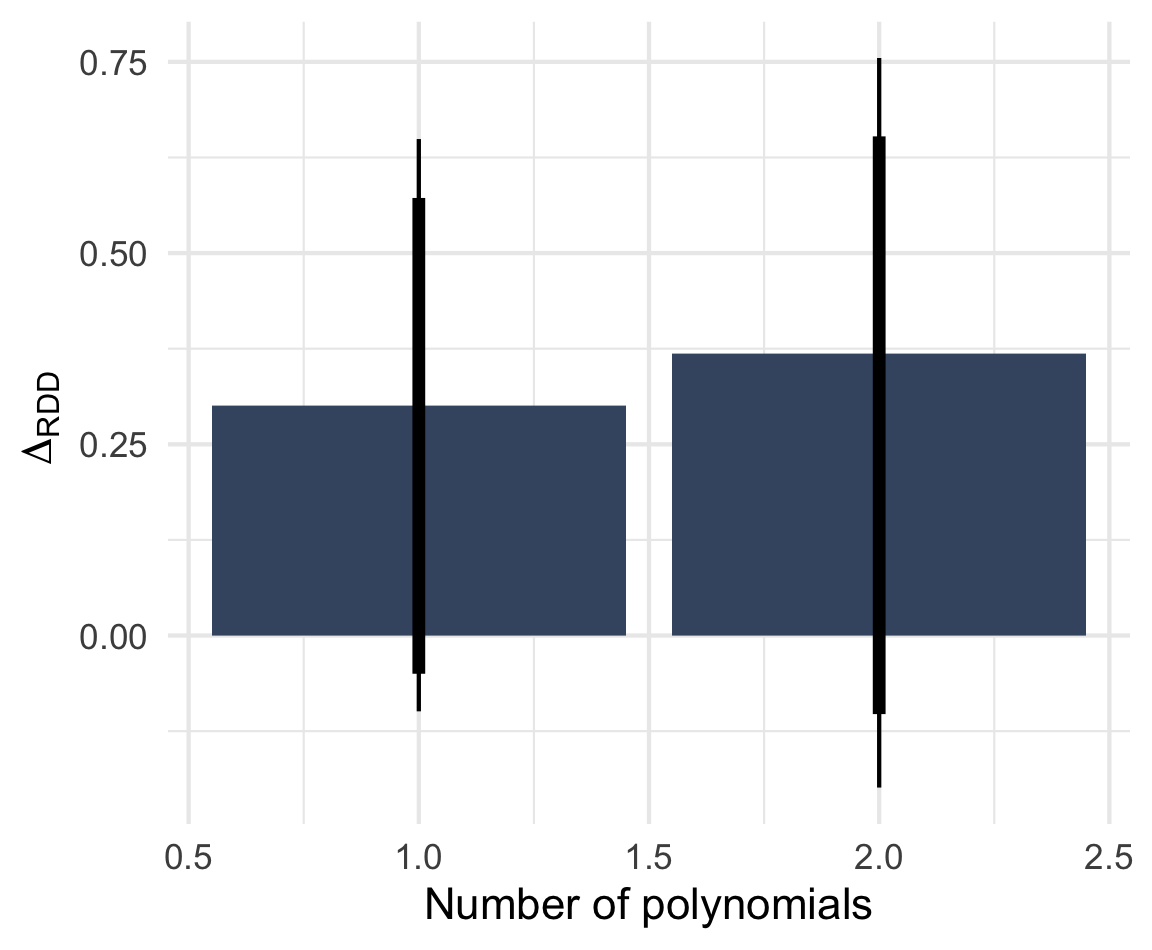
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent. n = 805 telephone calls (resp. 392 & 413) to 252 municipalities.
Conclusion
Immigrant minorities face discrimination in access to basic healthcare.
At least those with a West-African accent.Far-right mayors promote this type of discrimination.
Next step: 3 Mechanisms.
Conclusion
Immigrant minorities face discrimination in access to basic healthcare.
At least those with a West-African accent.Far-right mayors promote this type of discrimination.
Next step: 3 Mechanisms.

 Source: Romarri (2020)
Source: Romarri (2020)
Implications
For immigrant minorities
- More exploratory qualitative and field experimental work on further informal channels of welfare chauvinism.
- Excess prevalence of diseases that need preventive healthcare?
- Benefits and dangers of digitized administration?
Implications
For immigrant minorities
- More exploratory qualitative and field experimental work on further informal channels of welfare chauvinism.
- Excess prevalence of diseases that need preventive healthcare?
- Benefits and dangers of digitized administration?
For everyone
- "No one is safe until everyone is safe"
(Farrar and Ahuja, 2021)- Pre-reg hypothesis: Far-right mayors increased excess death rate during first wave Italian COVID-19 pandemic.
Thank you for your attention!
References
Calonico, S., M. D. Cattaneo, and R. Titiunik (2014). "Robust Nonparametric Confidence Intervals for Regression-Discontinuity Designs: Robust Nonparametric Confidence Intervals". In: Econometrica, pp. 2295-2326.
Farrar, J. and A. Ahuja (2021). Spike: The Virus vs. The People - the Inside Story. Profile Books.
Hemker, J. and A. Rink (2017). "Multiple Dimensions of Bureaucratic Discrimination: Evidence from German Welfare Offices". In: American Journal of Political Science, pp. 786-803.
Jørgensen, M. B. and T. L. Thomsen (2016). "Deservingness in the Danish context: Welfare chauvinism in times of crisis". In: Critical Social Policy, pp. 330-351.
Kitschelt, H. and A. J. McGann (1997). The radical right in Western Europe: A comparative analysis. Michigan: University of Michigan Press.
Romarri, A. (2020). Do Far-Right Mayors Increase the Probability of Hate Crimes? Evidence From Italy. SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 3506811. Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network.
Schaeffer, M. and M. Haderup Larsen (2022). "Who Should Get Vaccinated First? Limits of Solidarity during the First Week of the Danish Vaccination Programme". In: European Sociological Review, p. jcac025.
Appendix
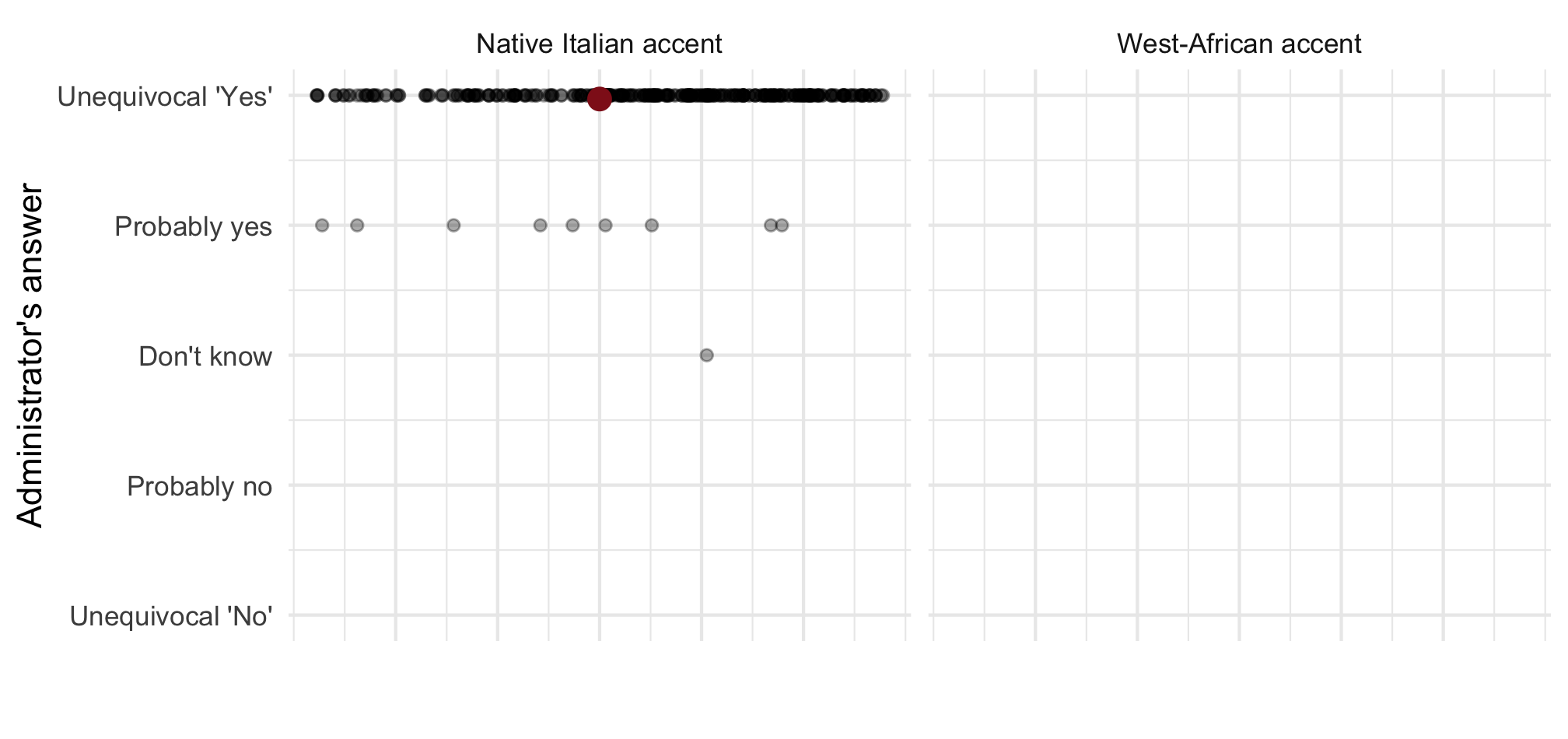
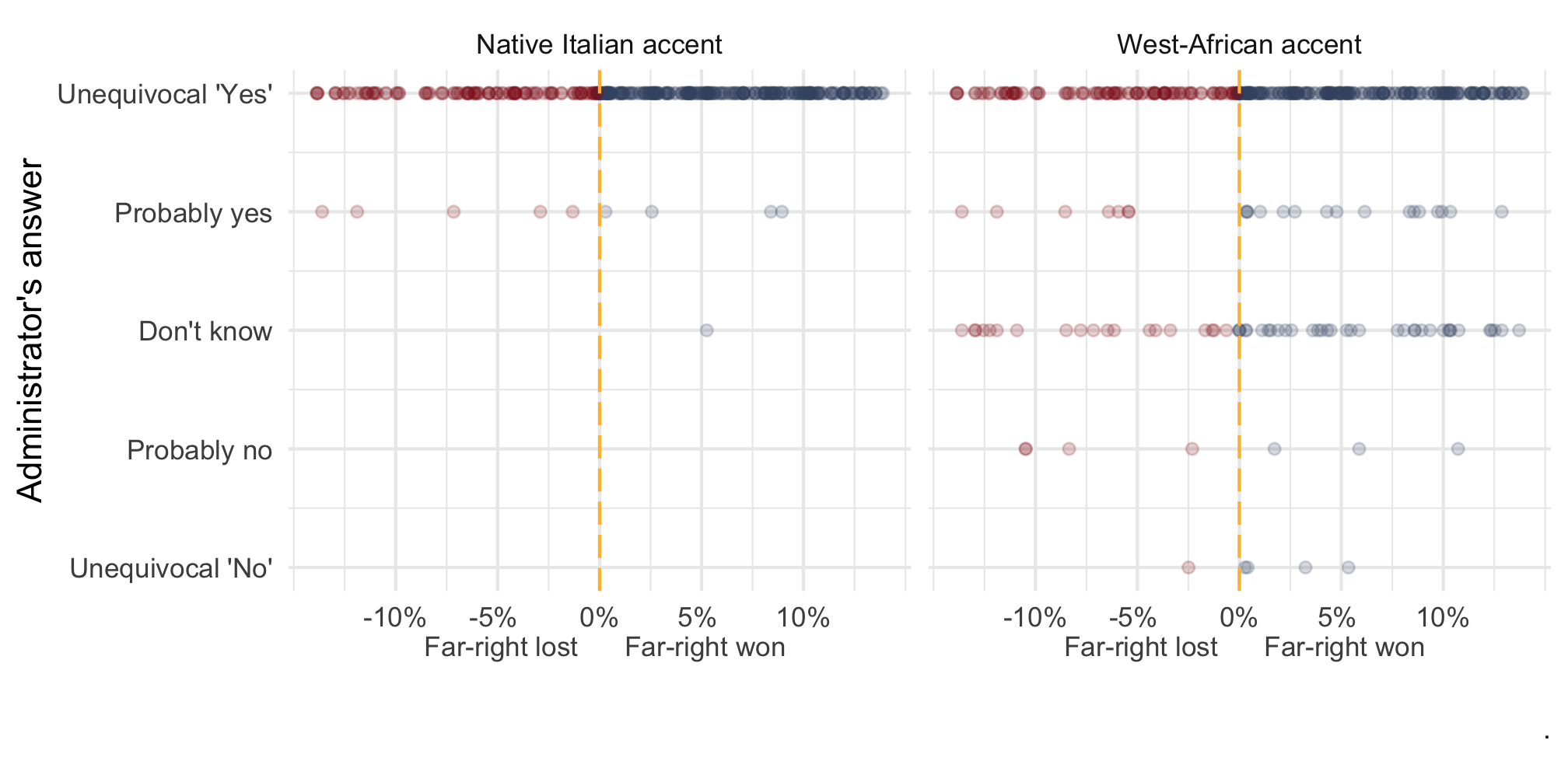
Binary success "Yes" & "Probably yes": 1; else: 0
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
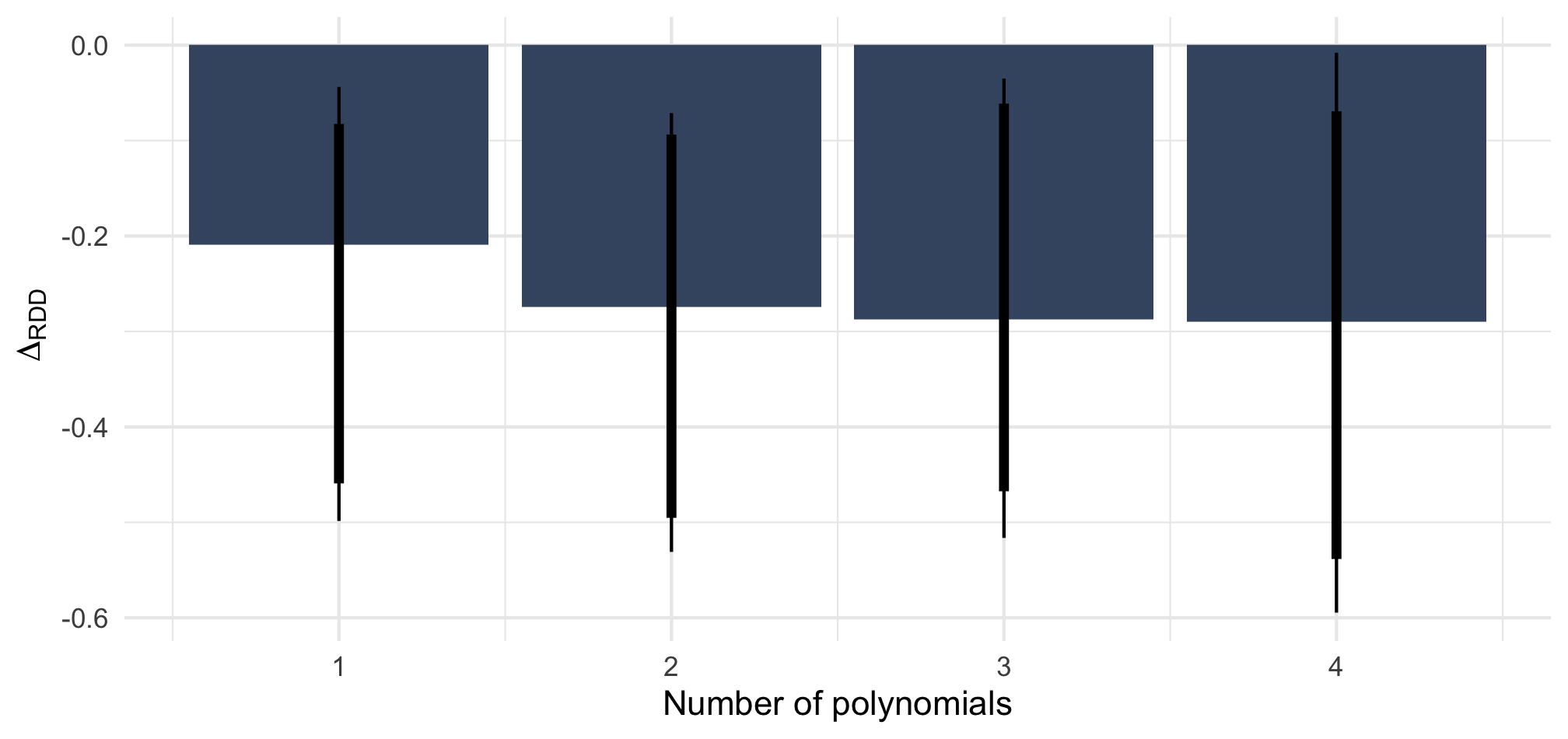
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Binary success "Yes", "Probably yes", or "Don't know": 1; else: 0
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
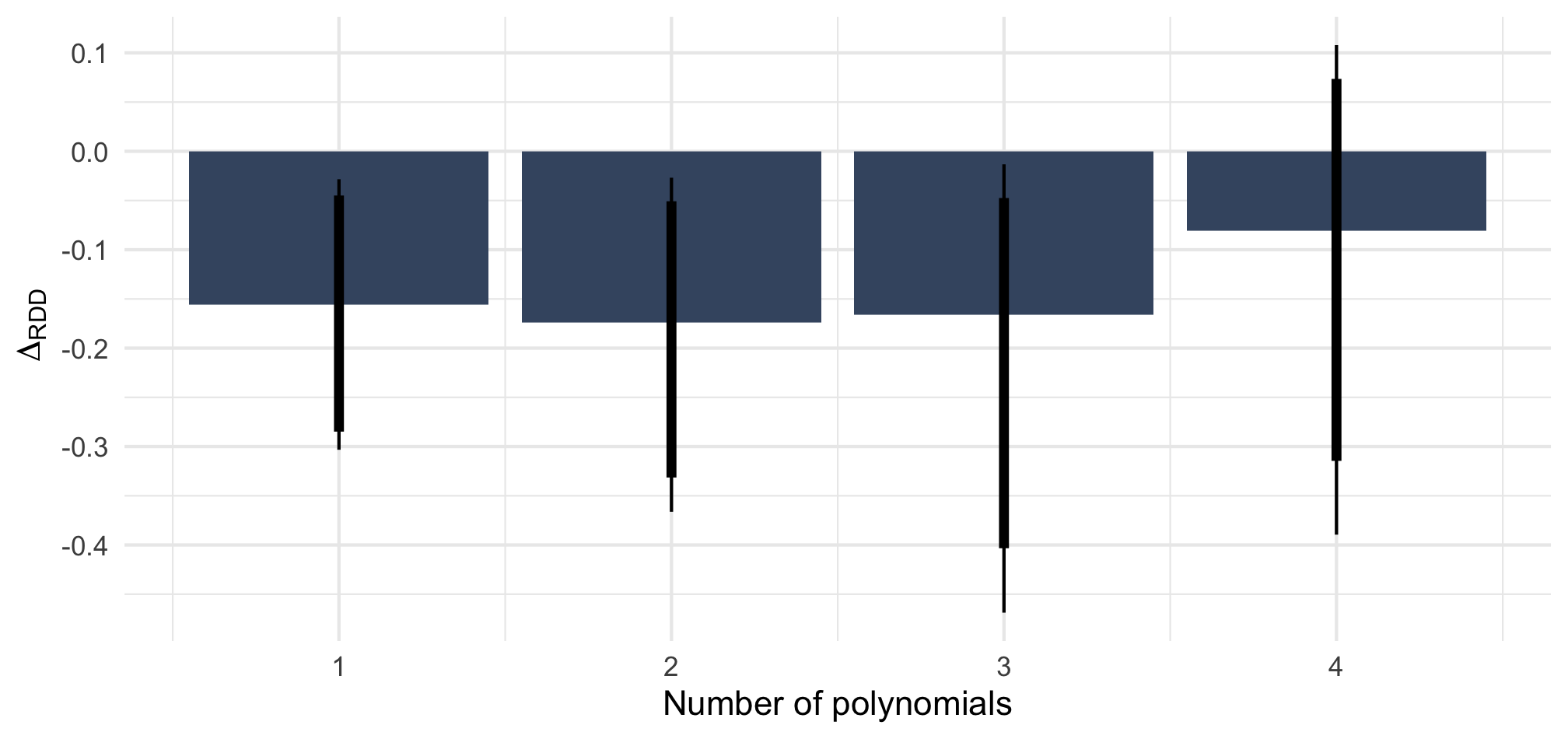
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
n = 812 telephone calls (resp. 391 & 421) to 257 municipalities.
Perfectly balanced data
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 54 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 492 telephone calls (resp. 246 & 246) to 123 municipalities.
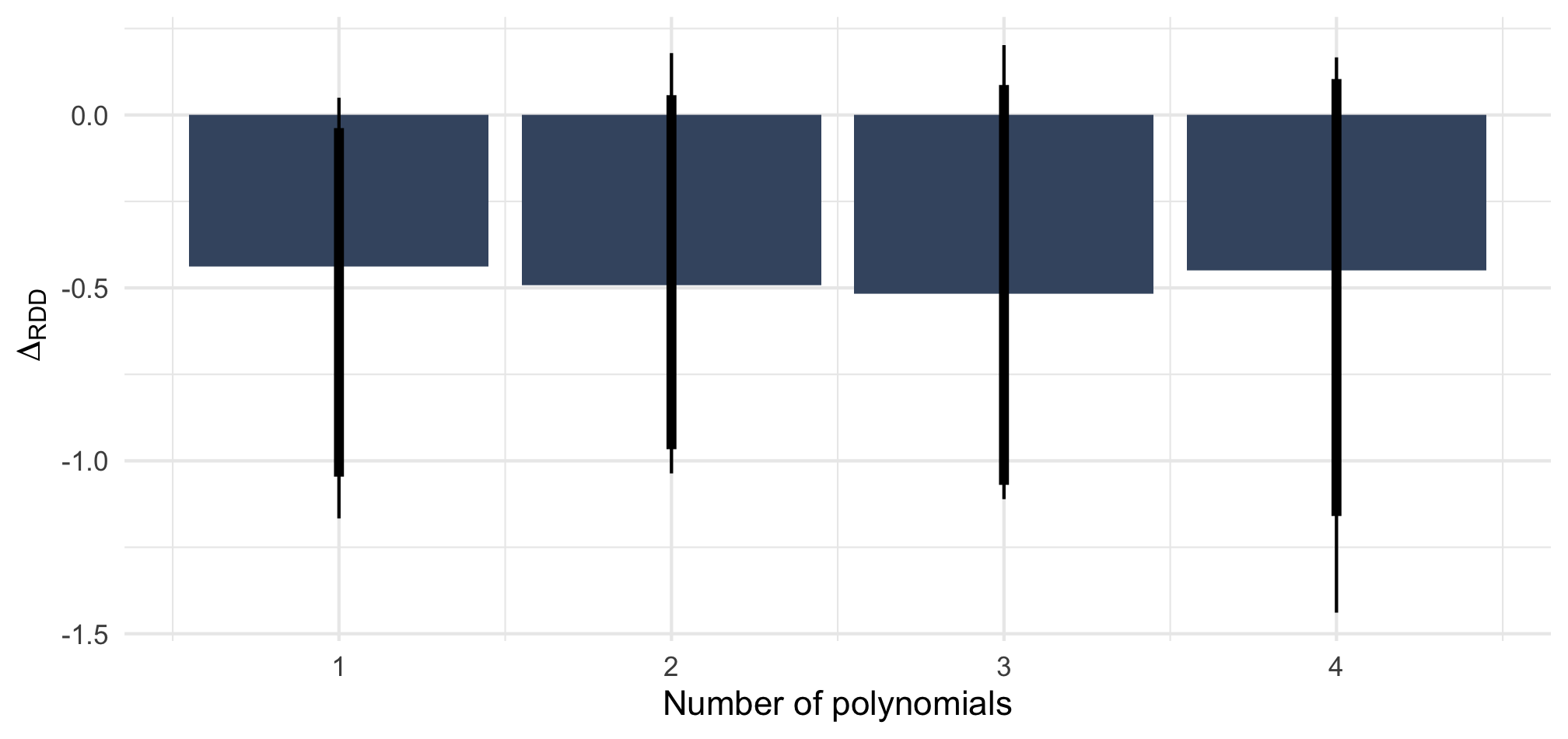
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
n = 492 telephone calls (resp. 246 & 246) to 123 municipalities.
Balanced data
Note: Point estimate with 90 and 95% CI based on OLS with standard errors clustered on the level of 72 regions. Adjusted for gender of the caller and municipality fixed effects. n = 686 telephone calls (resp. 343 & 343) to 220 municipalities.
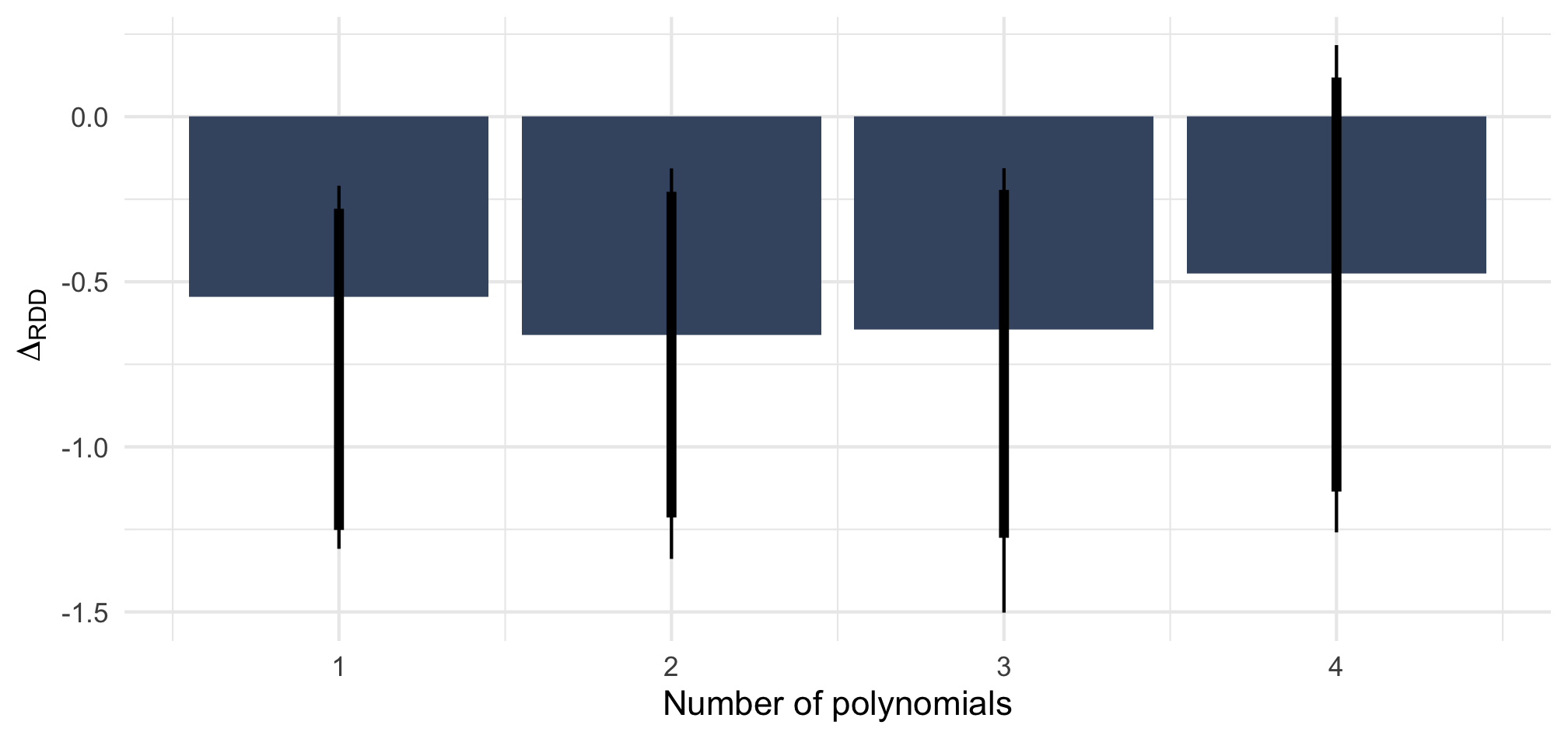
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
n = 686 telephone calls (resp. 343 & 343) to 220 municipalities.
Single rule versus in coalition
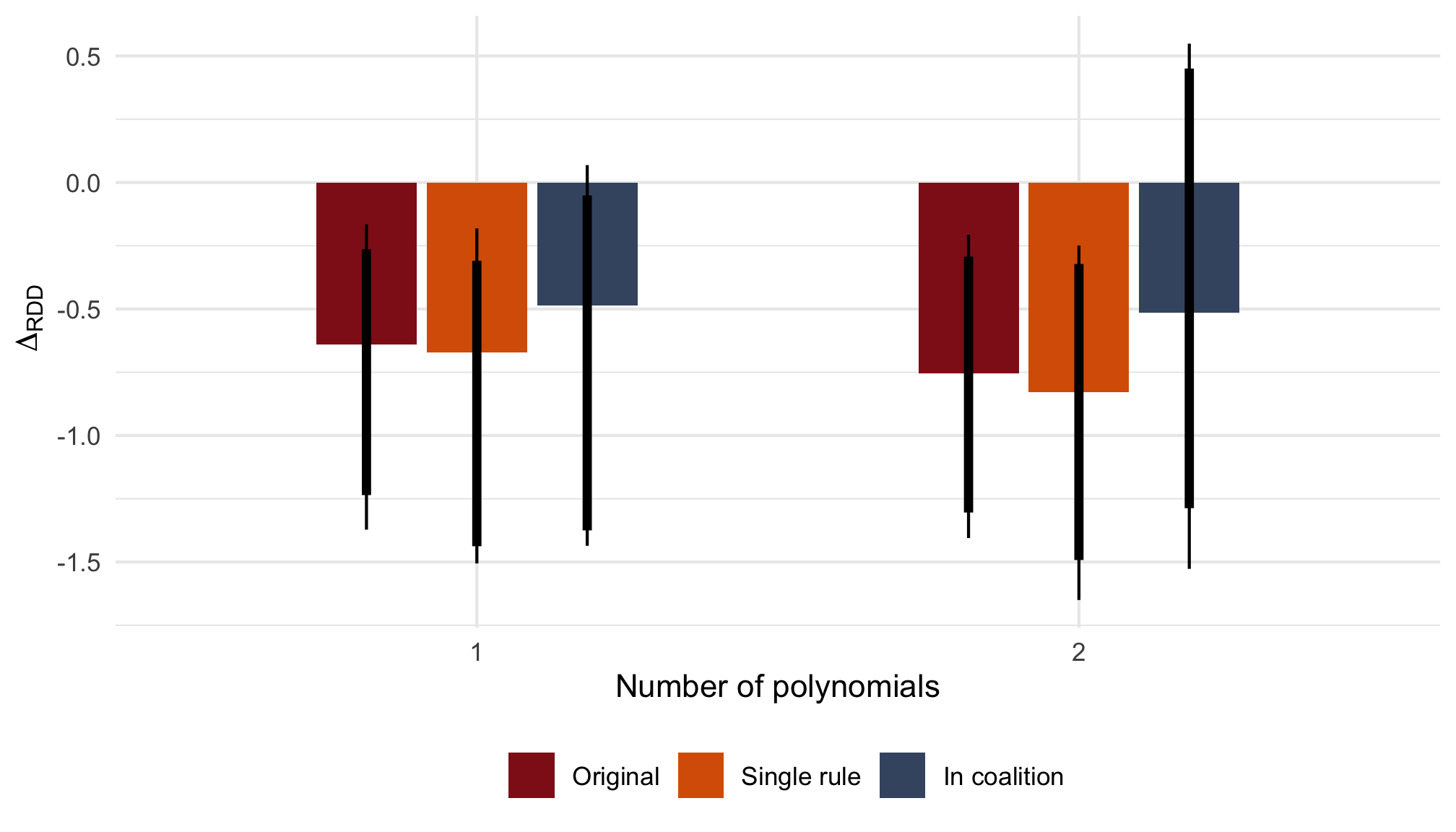
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
La Lega
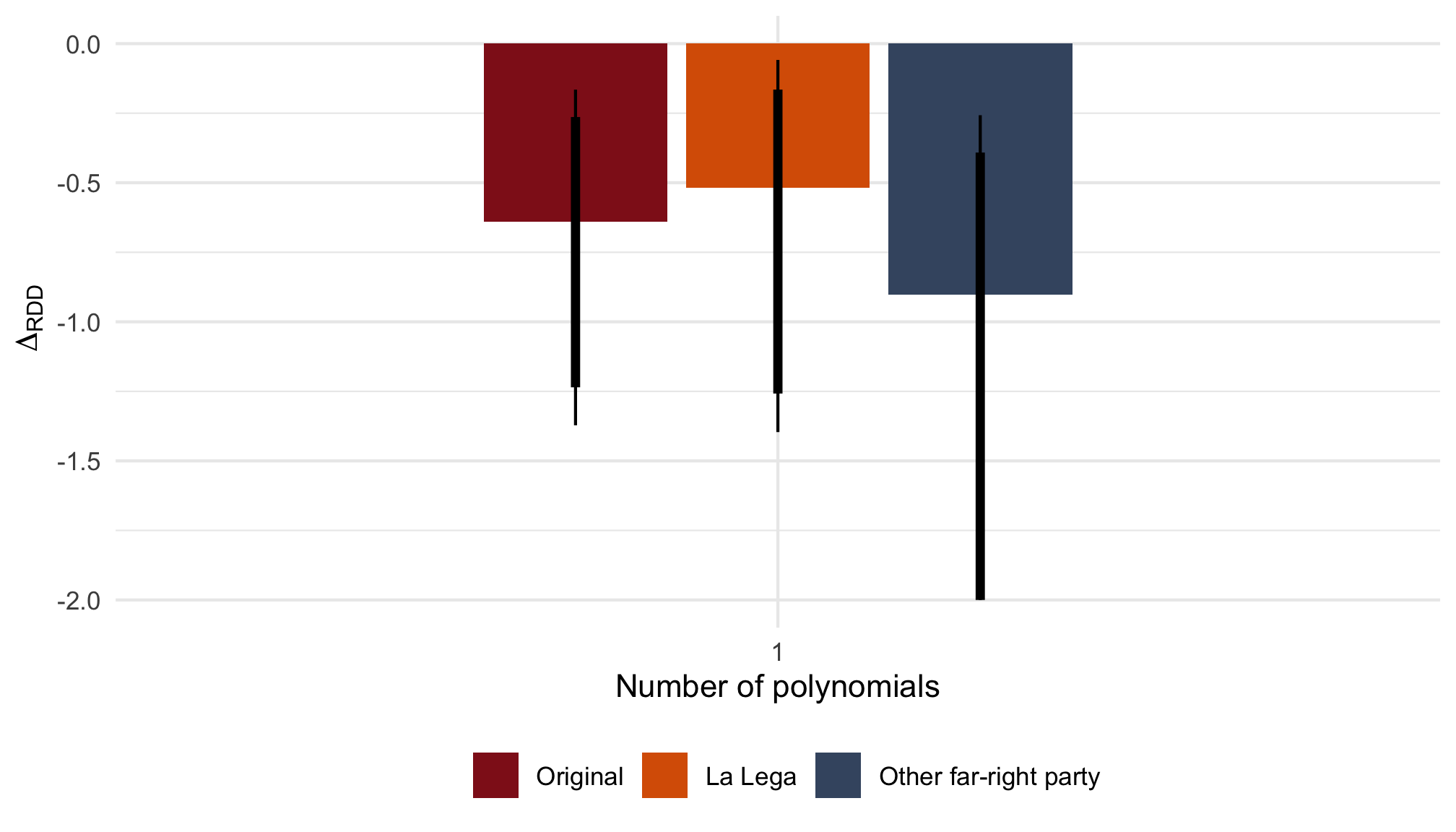
Note: ΔRDD estimates based on rdrobust() with 90 and 95% BCa confidence intervals (capped at -2) based on 2,000 bootstrap samples stratified by Italian/West-African accent.
RDD 1st election round
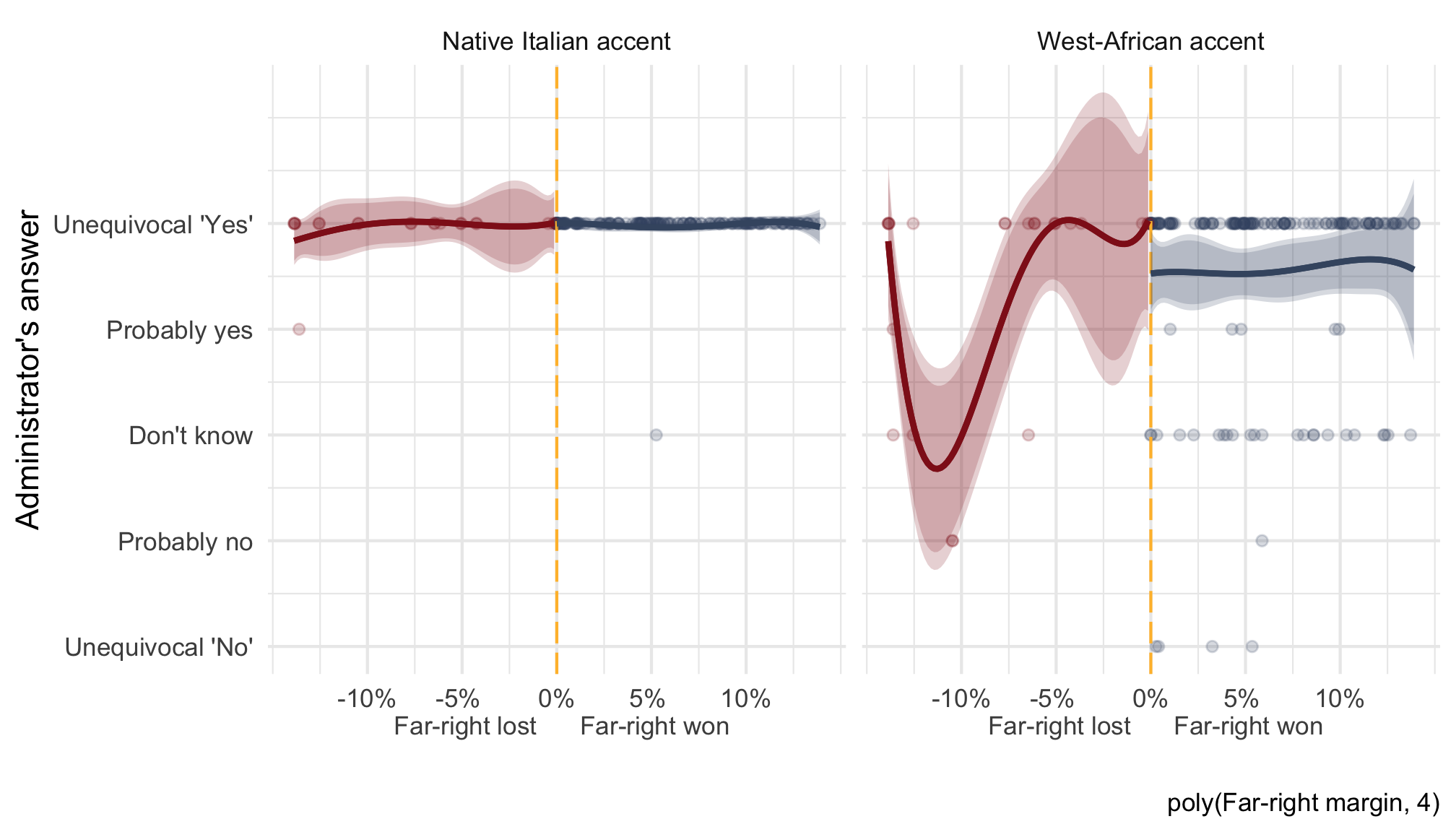
RDD 2nd election round